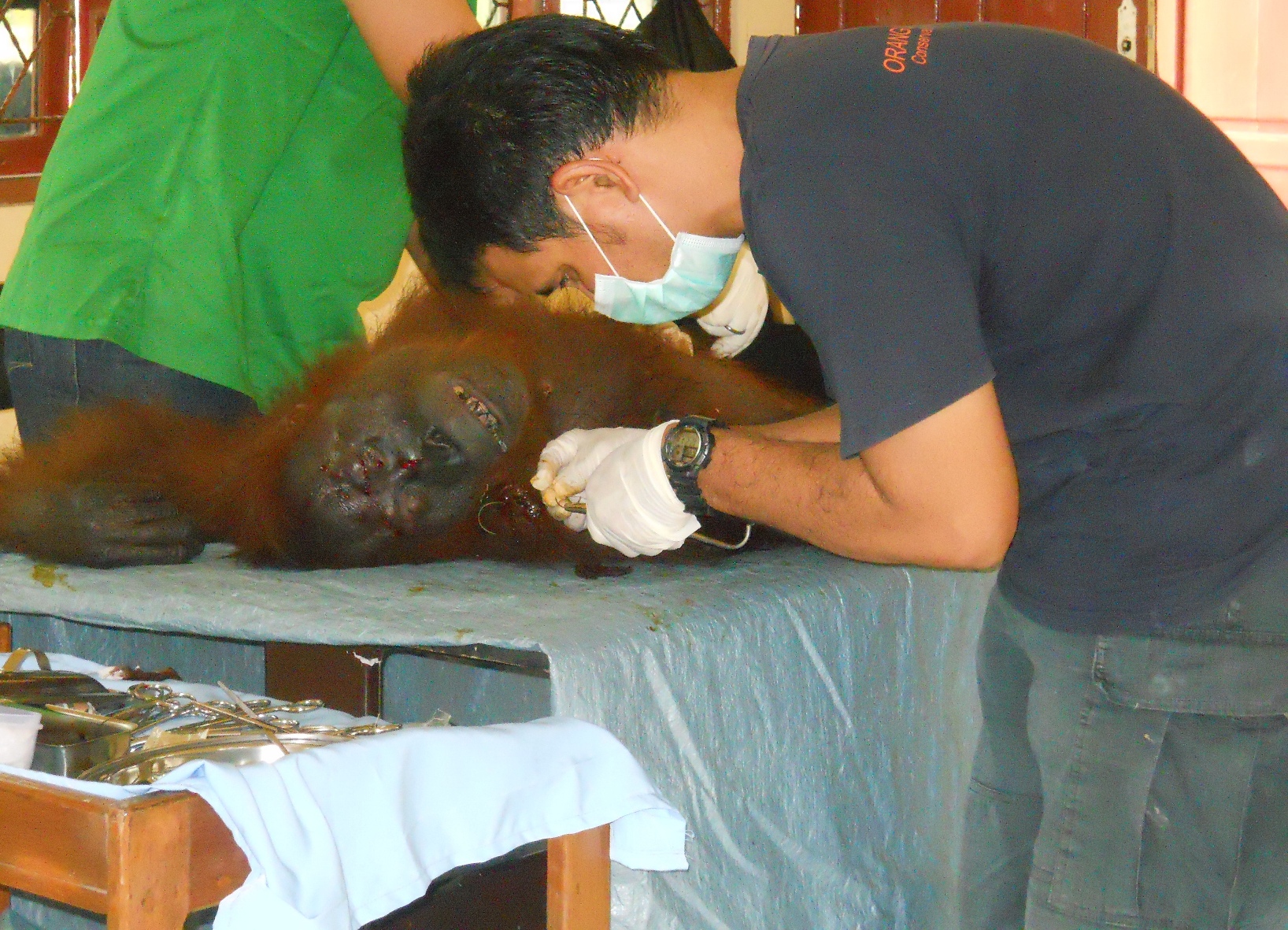
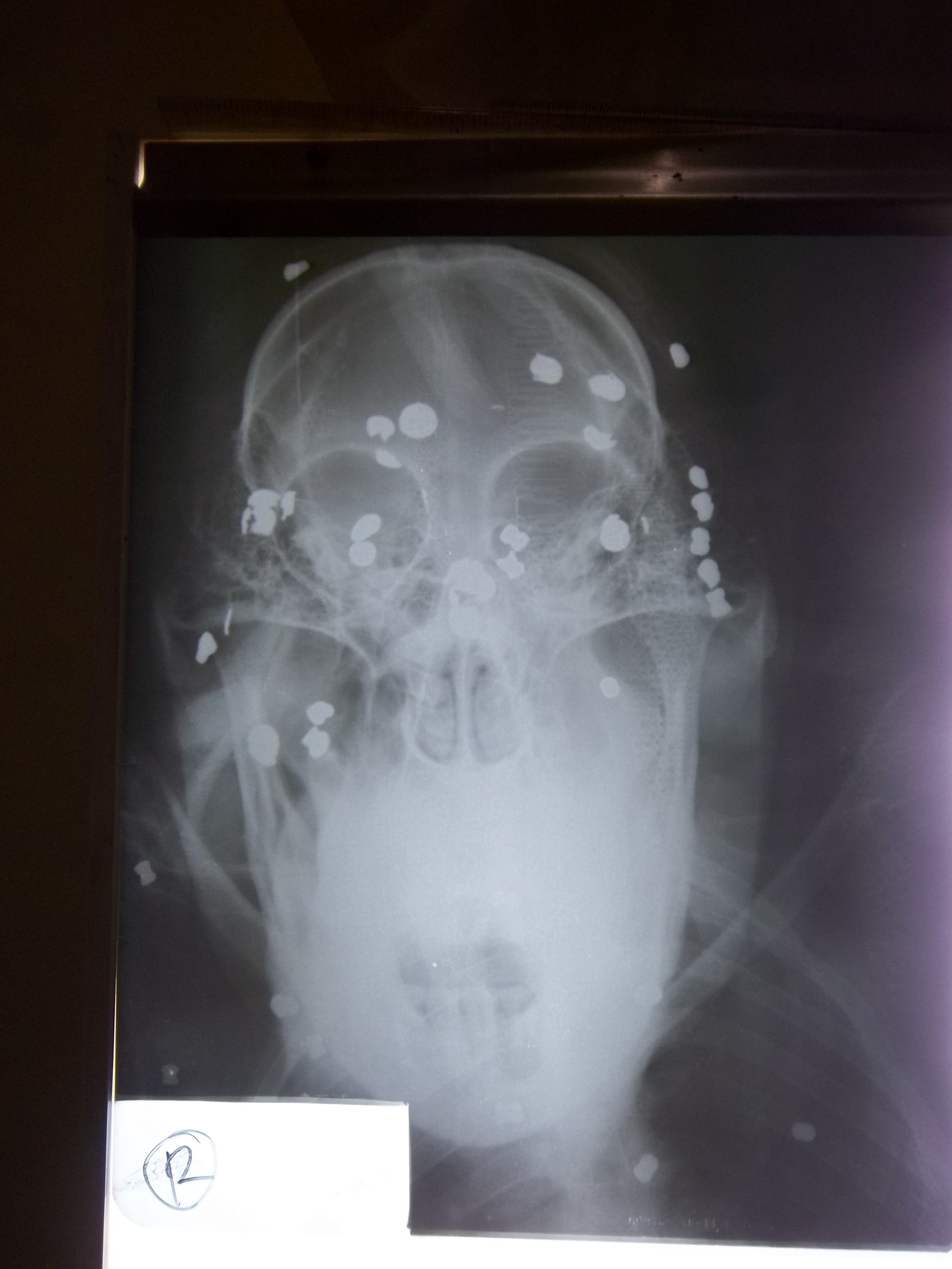
This article was published in the Independent newspaper today and covers the urgent situation in the Tripa Swamps, Aceh Sumatra. Read the full article with photos 'Oil boom threatens the last orang-utans'.
'A famous British company, Jardines, is profiting as the lowland forest – which shelters the few remaining orang-utans – is razed to make way for massive palm oil plantations, reports Kathy Marks in Tripa, Indonesia.
Tuesday, 23 June 2009
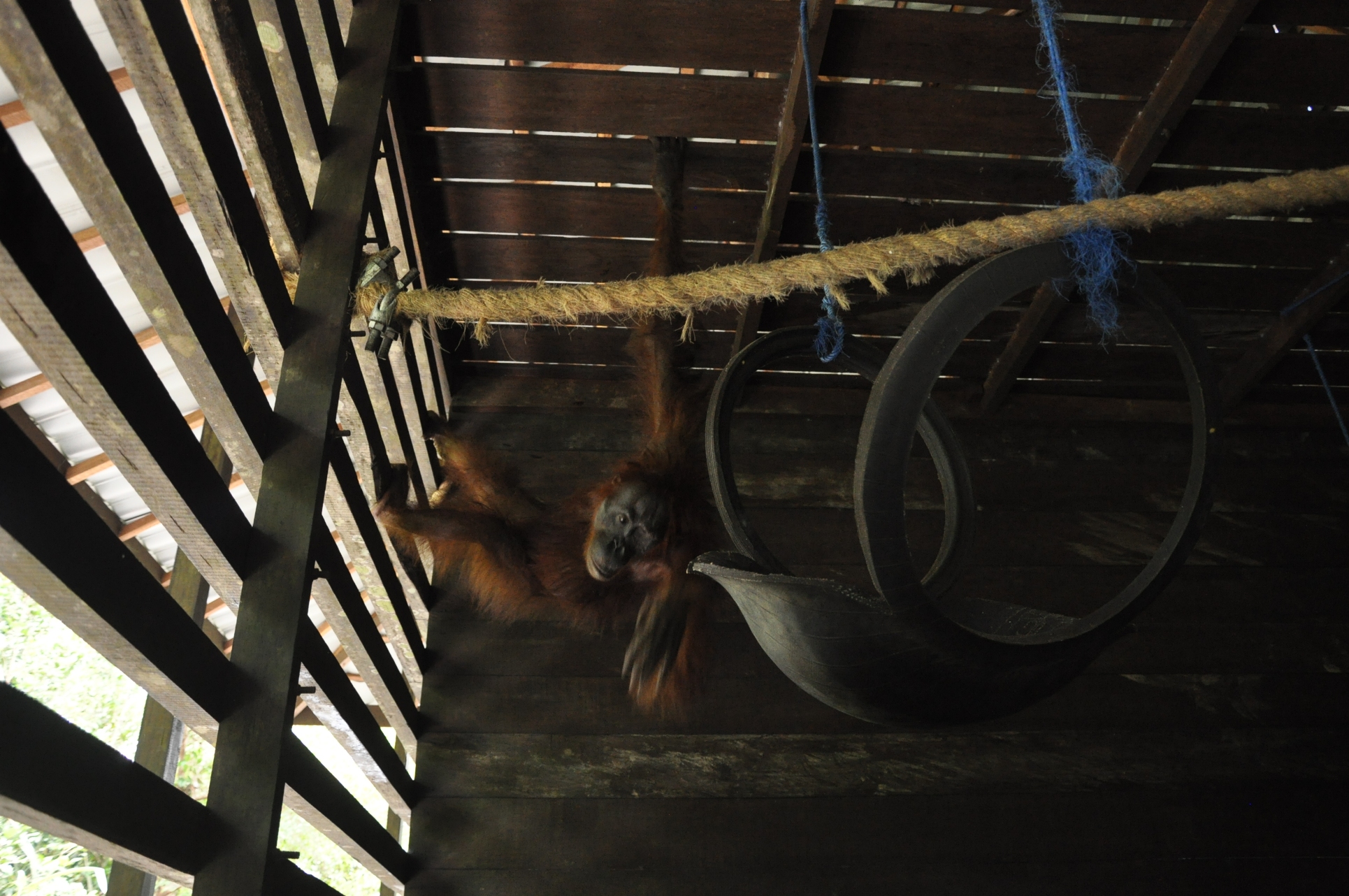
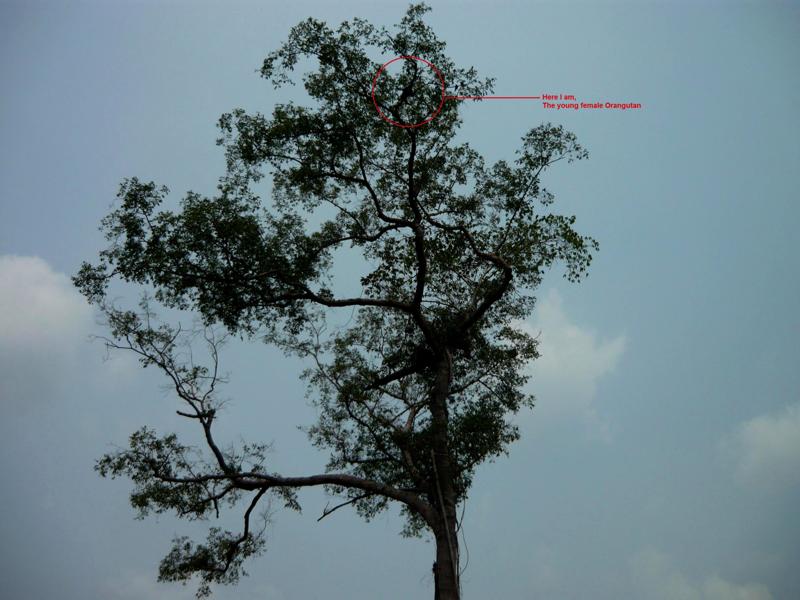
Perched halfway up a tree near a bend in the Seumayan River, a young orang-utan lounges on a branch, eating fruit. In the distance, smoke rises from an illegal fire, one of dozens lit to wipe out the virgin rainforest and replace it with oil palm plantations.
It's burning season on Indonesia's Sumatra island, where vast tracts of vegetation are being torched and clear-felled to meet the soaring global demand for palm oil. The pace is especially frenzied in the peat swamp forests of the Tripa region, one of the final refuges of the critically endangered orang-utan – and a company owned by one of Britain's most venerable trading groups is among those leading the destructive charge.
Prized for its productiveness and versatility, palm oil is used in everything from lipstick and detergent to chocolate, crisps and biofuels. Indonesia and Malaysia are the world's biggest palm oil producers – but they also shelter the last remaining orang-utans, found only on Sumatra and Borneo islands in the same lowland forests that are being razed to make way for massive plantations.
In Indonesia, one of the largest palm oil companies is Astra Agro Lestari, a subsidiary of Astra International, a Jakarta-based conglomerate which is itself part of Jardine Matheson, a 177-year-old group that made a fortune from the Chinese opium trade and is still controlled by a Scottish family, the Keswicks, descendants of the original founders.
Conservation groups are targeting supermarkets in Britain to alert consumers to the effects of the palm oil explosion. But The Independent can reveal that Jardines, registered in Bermuda and listed on the London Stock Exchange, is implicated through Astra Agro in ripping out the final vestiges of orang-utan habitat.
Environmentalists are dismayed by the activities of Astra Agro, one of the main companies operating in Tripa under permits that were awarded during the 1990s by the notoriously corrupt Suharto government. They point out that Tripa belongs to the nominally protected Leuser Eco-System, renowned for its exceptional biodiversity, and claim that the plantation businesses are contravening a logging moratorium as well as engaging in illegal practices including burning land.
Greenpeace UK says: "It's scandalous that a British company is bankrolling the destruction of Indonesia's rainforests and peatlands. We need to see big firms like Jardines withdrawing investment from companies involved in rainforest clearance."
Orang-utans are vanishing at an alarming rate in Borneo but in Sumatra their situation is even more precarious. The Sumatran orang-utan – more intelligent and sociable than its Borneo cousin and with a unique culture of tool use – is likely to be the first great ape species to go extinct.
There are believed to be just 6,600 individuals left, mostly living in unprotected areas of Aceh province. Their lowland forests remained relatively undisturbed during the long-running separatist war in Aceh, but since a peace agreement was signed in 2005, it has been open season.
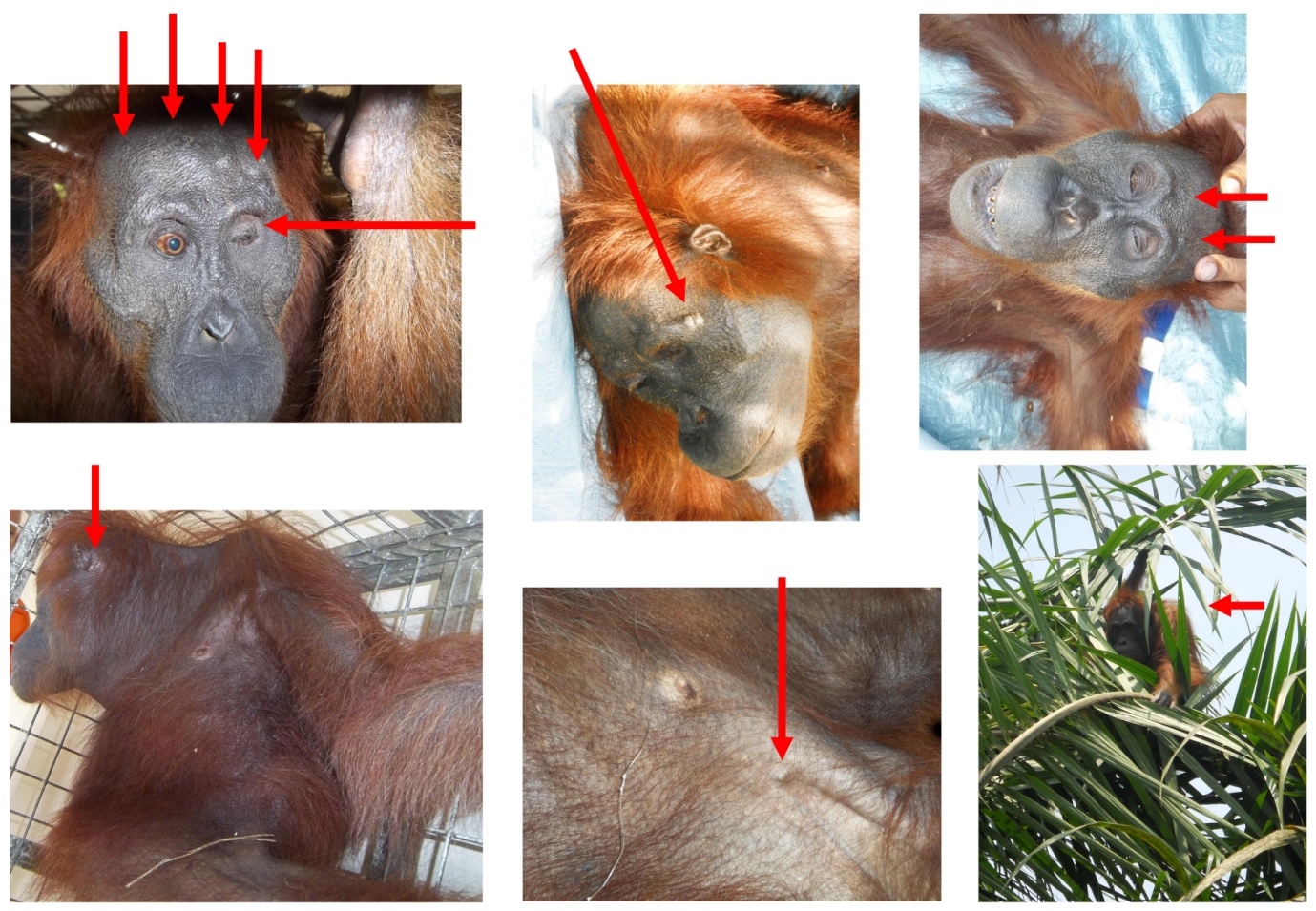
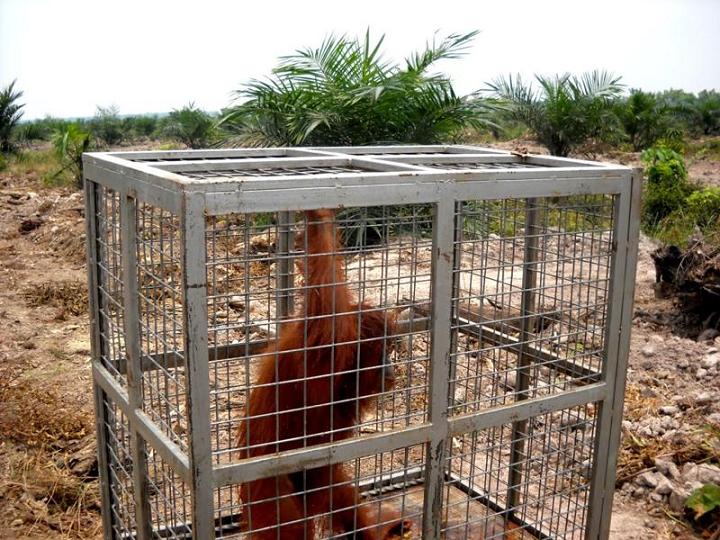
The primates are now splintered across 11 pockets of jungle, with only three populations considered viable. Another three, including Tripa, are borderline viable. Elsewhere, the orang-utans – which use sticks to extract insects from trees and seeds from fruit – are effectively extinct. As their territory shrinks, along with their food supplies, the apes are increasingly coming into conflict with humans. Farmers shoot those caught raiding crops; babies are captured and sold as pets. Adults discovered in oil palm plantations may be hacked to death with machetes.
In Tripa, more than half of the 62,000 hectares of ancient forest has gone. As well as being home to endangered species including the sun bear and clouded leopard, the peat swamps acted as a protective buffer during the 2004 tsunami. They also hold gigantic carbon stocks which are now being released, exacerbating climate change. "If you can't save Tripa, what can you save?" asks Denis Ruysschaert, forest co-ordinator for PanEco, a Swiss environmental organisation.
Sumatra is a beautiful island, with jungle-clad mountains and picturesque villages where long-horned water buffalo wander. But it is difficult not to be shocked by the colonisation of the landscape by one short, stumpy tree: oil palm. The monoculture is a desolate sight, stretching for miles, relieved only by charred hillsides dotted with tree stumps – cleared land awaiting yet more oil palms. Trucks rattle past, laden with the prickly red fruit from which oil is extracted. In Aceh, they call it the "golden plant" – the cash crop that is lifting the province out of poverty and helping it rebuild after the tsunami. "Recently there's a frenzy to plant oil palm," says Fransisca Ariantiningsih, who works for Yayasan Ekosistem Lestari (Yel), an Indonesian conservation group.
On Sumatra's west coast, a small-time farmer, Raluwan, is nursing his seedlings. Ten families, he explains, have logged and burnt 100 hectares of land. Each hectare will yield four tonnes of fruit, fetching 800 Rupiah (47 pence) a kilo."I used to grow chilli, but palm oil is a very economical crop," he declares. "You don't need much pesticide or fertiliser." Raluwan knows orang-utans live in the nearby forests. "I don't care," he says. "I've got to feed my family."
However, many are missing out as the industry grows to meet demand from Europe, the US, China and India. Most plantation workers are migrants from Java and in Tripa, communities that depend on the swamps for water, fish and medicinal plants are suffering.
Kuala Seumayan is hemmed in by plantations. Villagers say they no longer have space even to bury their dead. "Since the forest has been chopped down, it's difficult to get food," says one elder, Darmizi. In the Seumayan River, youngsters dive for freshwater clams while children squeal and splash in the placid brown waters. It's an idyllic scene, but something is missing: the sights and sounds of the forest. The only wildlife consists of a hornbill and two long-tailed macaques. Indrianto, a forestry manager, says: "This used to be all peat swamp, with many trees and animals. Now it's all oil palm. Before, I heard animal calls. Now I hear only chainsaws."
By chance, we spot an orang-utan in a solitary tree. Tripa has just 280 apes left. The young male, its fur glowing in the afternoon sun, curls one arm lazily over an upper branch.
A black slick floats on the water: sludge from one of many canals dug to drain the swamps. The arduous procedure is considered preferable to planting on fallow land, which would require negotiations with landowners. This way, the companies also get to sell the timber. As you fly over Tripa, the scale of destruction becomes clear. The green tangle of the forest, in all its riotous variety, abruptly gives way to giant rectangles, laid out with geometrical precision and studded with thousands of palms.
Riswan Zen, a spatial analyst for Yel, last flew over in 2007. "So much forest gone, and all in two years, my God," he says, gesticulating at a satellite imaging map. "If nothing is done, there'll be no forest left in one to two years."
Tripa, designated a priority conservation site by the UN, could hold 1,500 orang-utans if the forest was allowed to regenerate. Prospects seem slim, although Indonesia – one of the world's biggest emitters of greenhouse gases, thanks to deforestation – claims to be committed both to saving the orang-utan and combating climate change.
Fewer than a quarter of Indonesian producers have joined the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil, a global organisation promoting sustainable practices. (Astra Agro is not among them.) Even in Aceh, where Governor Irwandi Yusuf, a former rebel leader, has proclaimed a "Green Vision", authorities seem unwilling to crack down on the powerful oil palm companies.
So far, Jardines, whose colourful history inspired a series of novels by James Clavell, has resisted pressure to rein in its Indonesian subsidiary. In a statement to The Independent, Jardines – whose interests include the Mandarin Oriental hotels and Asian branches of Starbucks and IKEA – said Astra Agro's plantations "function in full compliance with ... environmental impact studies".
Astra Agro says it plans to develop only half of its 13,000 hectares in Tripa because of conservation concerns, and it denies any illegal activity.
Ian Singleton, a Briton who heads PanEco's Sumatran Orang-utan Conservation Programme, has no doubt that oil palm is the biggest threat to the orang-utan: "I see the orang-utan as a test case. Are we serious about trying to conserve the planet's eco-systems? If we are, let's prove it by saving a species like the orang-utan. We know where the orang-utans are; all we have to do is protect the forests. If we're serious about conservation, this is where we start."
At a glance: Jardine Matheson
*Founded by two Scottish traders in Canton, China in 1832, it was the first British trading company to smash the East India Company's Asian monopoly.
*Founder William Jardine was known as "the iron-headed old rat" for his toughness and asperity.
*The company's fortunes were founded on smuggling huge quantities of opium into China, creating millions of addicts.
*When the Chinese fought back, Jardine persuaded the British government to launch the First Opium War against China.
*Astra Agro, a subsidiary of the company, claims that "concern for the environment" is "an integral part of all the company's activities".