The reappearance of long-lost orangutan, Andy! In this orangutan story we explore where Andy has been, as well as his unusual upbringing as an adopted orangutan.
News from Sumatra - An update from our partners at SOCP
Please read the orangutan update below written by our partners at the Sumatran Orangutan Conservation Programme. Together we are working to protect the habitat and future of all three critically endangered species of orangutan:
On Wednesday 26th August, 2020, the orangutan post-release monitoring team at the SOCP’s Jantho orangutan reintroduction site, in Aceh province, came across an adult female orangutan. After a quick check to see if they could figure out who it was, they noticed that she was carrying a young infant, no more than a few months old! The baby orangutan is male and is the third baby orangutan born in Jantho since the SOCP's Orangutan Reintroduction Programme began releasing orangutans into the Jantho Nature Reseve in 2011. Mother and baby both appear to be healthy and are behaving just like wild orangutans would. The infant is being carried properly by his mother and has been seen breastfeeding without difficulty on numerous occasions.
After checking some earlier photographs the team are confident the mother is 'Edelweiss', actually the very first orangutan to be released at Jantho back in 2011. After her release she immediately moved away from the camp area and deep into the forest. On February 11, 2020, a female orangutan strongly suspected to be Edelweiss was observed not far from the orangutan reintroduction site and at that time she was showing signs of being pregnant.
The aim of SOCP's orangutan release program at Jantho is to build a new, wild population of Sumatran orangutans (pongo abelii) as a "safety net" or "backup", should a of catastrophe befall the remaining truly wild populations in and around the Leuser Ecosystem. This is especially important in the midst of the current pandemic, as whilst the scientific evidence suggests orangutans and the other great apes are susceptible to infection by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the effect it might have on them remains entirely unknown.
To date, more than 120 individual orangutans have been successfully released into the Jantho Nature Reserve but many more are needed before the population could be considered genetically viable and self-sustaining for the long term. For this reason, every orangutan released or born in Jantho’s forests is extremely significant and important, and gives new hope for the future of this critically endangered species.
Director of the Sumatran Orangutan Conservation Programme, Dr Ian Singleton said “We always knew it would be several years before we really started to see infants being born on a regular basis among the new population of orangutans we are creating in Jantho. This is because most of the orangutans we release there are 5 to 8 years old, whilst wild orangutan females tend to be around 15 years old on average when they have their first infant. It's great to see these new infants starting to appear though, and it's especially rewarding when you think about all the hard work, spanning many years, that goes into reintroducing each and every one of the orangutans we have released to date. That these new infants have never known captivity and human contact is also extremely heart-warming, and hopefully they never will, unlike their parents, whose own mother’s were almost certainly killed during their original capture and some of whom have endured years chained by the neck or kept in tiny cages at the hands of their illegal owners. The orangutans we are releasing in Jantho, and those now being born there, really are the founders of this entirely new wild population, and it's never been more important to have these ‘back up’ populations as we face the extremely worrying prospect of SARS-CoV-2 infections passing from humans to orangutans, both in captivity and in the wild”.
Photos by Kike Arnal/Arcus Foundation
Our new partnership to protect all three species of orangutan
Orangutan Foundation is pleased to announce that we have entered into a new partnership to support the Sumatran Orangutan Conservation Programme, which has been operating in Sumatra for the past 20 years.
Whilst we have supported this programme in the past, this new partnership will ensure that in the future, the Foundation is more effective in its efforts to help conserve all three critically endangered species of orangutan - Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutans.
We will now be including news updates from Sumatra and Borneo in our e-news, blogs and social media posts.
Photos by Kike Arnal/Arcus Foundation
30 years and counting
This year at the Foundation we are celebrating an important milestone- 30 years of conservation.
30 years protecting the critically endangered orangutan. 30 years on the front line guarding the vulnerable tropical forests of Borneo. 30 years collaborating with local people with environmental education and sustainable land-management practices.
The Orangutan Foundation’s programmes and primary focus is in Central Kalimantan, Indonesian Borneo. Our country office in Pangkalan Bun is responsible for the livelihoods of 55 staff, all of whom are Indonesian from local towns and villages. This means that our dedicated workforce are fully appreciative of their surrounding environment and understand the importance of protecting their nearby forests.
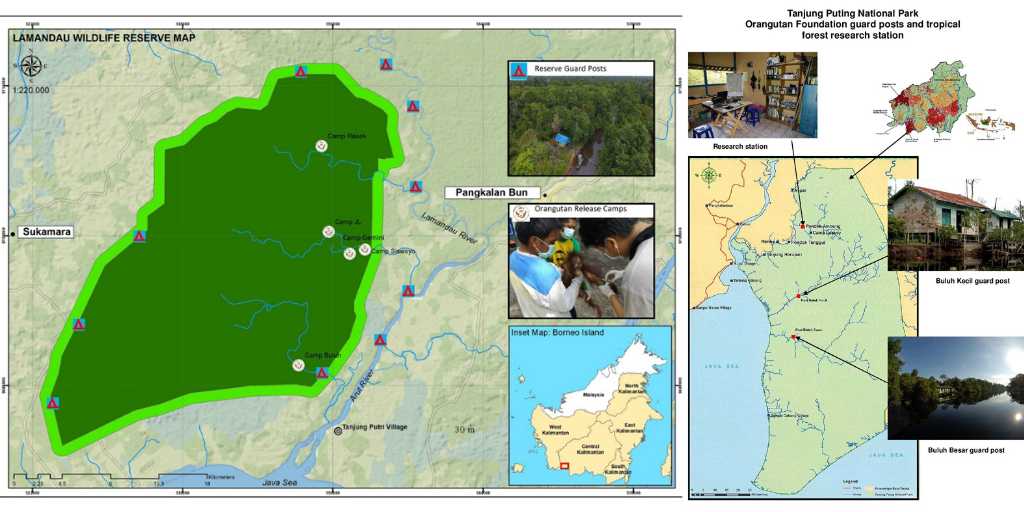
In spite of the difficulties that we are currently all facing around the world, the threat to tropical forests in Borneo remains a constant, and our 10 guard posts are still alert to monitor any cases of illegal activity. These posts contain fire-fighting equipment and continue to play a vital role in protecting over half a million acres of forest across the Lamandau Wildlife Reserve and Tanjung Puting National Park (below).
The Foundation’s five post release monitoring camps within the Lamandau Wildlife Reserve (above left) continue to oversee reintroduced orangutans and the 10 young orphans currently in our soft-release programme. These orphans have been rescued from a life in captivity and offered a new chance of a future in the wild by learning essential skills in the safety of a protected forest.
Elsewhere in Tanjung Puting National Park, our remote camera traps are recording a fascinating insight into the diverse forests surrounding Pondok Ambung Tropical Forest Research Station (above right). Clouded leopards, tarsiers, sun bears, proboscis monkeys, and false gharial crocodiles are a handful of the unique species that continue to be observed and studied closely here.
Meanwhile, our Habitat Restoration Programme has also been active in recent months. To date over 75,000 tree saplings have been planted since the devastating forest fires of 2015, and our team of experts are still diligently cultivating a new generation of saplings to reintroduce into the wild. We hope that these young plants which are more resistant to fires, will soon help rejuvenate new patches of forest and form part of a healthy natural ecosystem for years to come.
The Orangutan Foundation operates in Indonesia under an MoU with the Ministry of Environment & Forestry and has a responsibility for our own field programmes. We were also the first organisation in the UK to raise awareness of the critically endangered orangutan and its threatened habitat 30 years ago. Despite the challenges that we face today, at the Foundation we know that we can continue our vital work long into the future. If you can, please help us maintain our important ongoing programmes by sponsoring an acre of tropical forest, adopting an orphaned orangutan, or making a donation today.
Our progress relies on the kindness of our supporters, members, and partners, so thank you for your dedicated support.
Volunteering in Belantikan - A Dayak Perspective
During our time in Belantikan we were also fortunate enough to have the opportunity to have some long conversations with some of the older villagers about their way of life. We visited the ladang of Pak Taryom outside the village of Nanga Matu, to see the new crops he is cultivating with Yayorin’s help and find out how their new methods are bringing benefits to the area.

Pak Taryom in his ladang near Nanga Matu, cultivation here has been much changed with Yayorin's help
Pak Taryom also explained to us about the traditions and ceremonies of the Dayak people. His brother, Pak Maju, is the last man of Nanga Matu refusing to convert to one of the five state approved faiths of Indonesia and still clinging to Kaharingan – the traditional Dayak religion. He is also the father of Yayorin’s cook Ani, the youngest of his seven daughters.
Pak Maju lives outside Nanga Matu and, on our last day in Belantikan, we went to visit him at his ladang tucked away inside the forest. He’s 58 years old and still working in the fields. We found him sat under a tarpaulin sheet in the centre of his ladang, a thin line of smoke twisting to the sky from the fire he was sitting by chewing tobacco rolled in leaves, a rifle and a long knife by his side. I got a little perturbed at one stage during our conversation when he turned to me and mimed pulling off my head and drew his knife. Although it turned out, via translation, that he was just explaining that when a Dayak is angry they can pull off an enemy’s head with their bare hands without recourse to a blade.
Pak Maju - Nanga Matu's last adherent of the Kaharingan religion in his ladang
Pak Maju also told us how the villagers of Nanga Matu and Bintang Mengalih still come to see him and ask him to summon the spirits to grant their wishes. Nevertheless, it seemed to me that he could accept the end of the Kaharingan culture, religion being in his mind a matter of personal choice. He could not, however, accept the destruction of the forest. When we asked him what he thought of it he told us that the balance of life has been upset and ‘when the trees and the hills are all gone [to logging and mining] the people will all die.’. The world around Pak Maju is changing so fast that his fears for the forest, and everything that lives within it, could be realised within his lifetime.
We left Belantikan full of great memories. The work of the Orangutan Foundation, Yayorin and the local communities to protect this area for the benefit of people, orangutans and the forest continues.
Thank you,
David