Please see our press release below about our Trustee's new film, Terry Pratchett Facing Extinction, showing tonight on BBC2 at 9pm.
PRESS RELEASE
Terry Pratchett Facing Extinction
BBC2 9pm Wednesday 27 March 2013
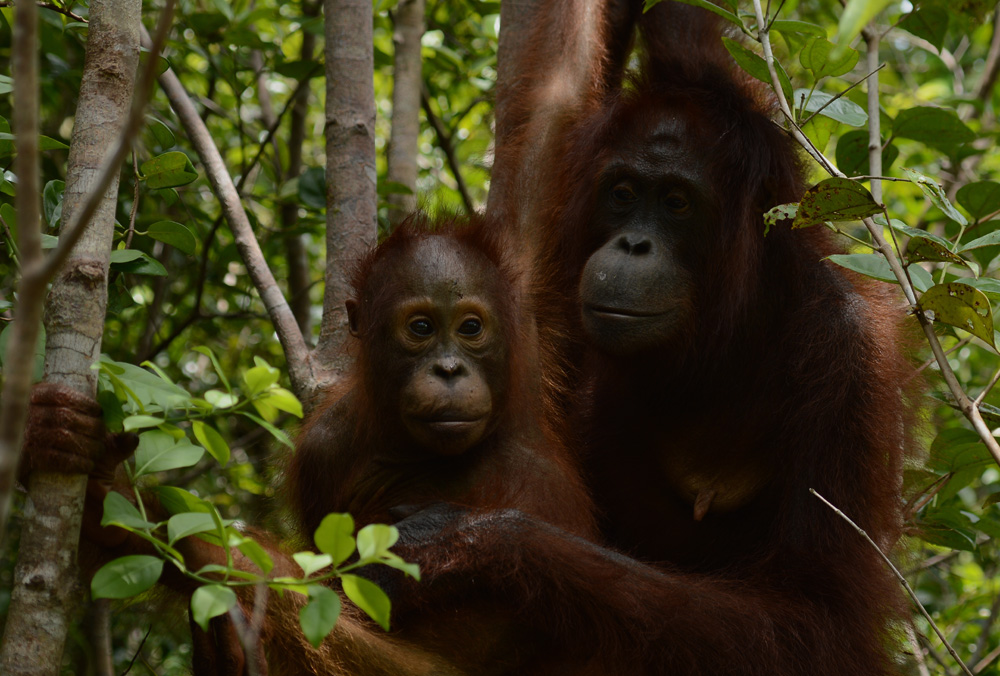
Terry Pratchett hears the orangutans’ long call
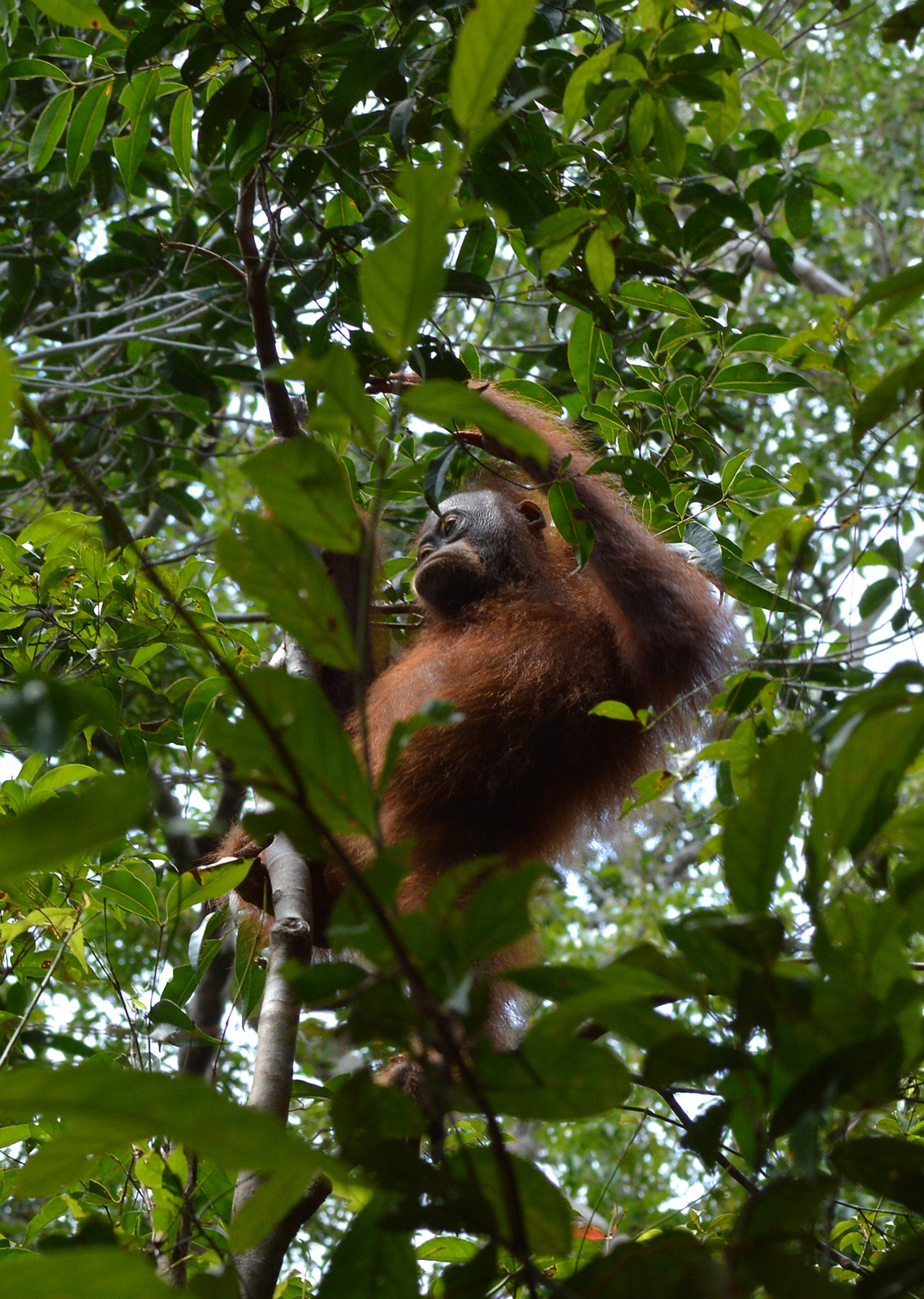
Sir Terry Pratchett, fantasy author and Trustee of the Orangutan Foundation, returns to the forests of Borneo to see what hope there is for the endangered orangutan whilst facing his own personal challenges.
Sir Terry Pratchett encountered wild orangutans for the first time in 1994 whilst filming Terry Pratchett’s Jungle Quest. One ape, Kusasi, who was the dominant male “king of the jungle” at the time, left a lasting impression that would, almost two decades later, entice Terry back to Borneo. In his latest film, Terry Pratchett Facing Extinction, to be aired on BBC2 9pm on 27 March, Terry explores not only the fate of the endangered orangutan but also his own fate as he battles with a rare form of Alzheimer’s.
Terry Pratchett is best known for his hugely popular Discworld novels, a fantasy series, which feature the Discworld character The Librarian, who was transformed into an orangutan. This prompted Terry’s curiosity about the great red ape, which he has described as “having a face like a surprised coconut”, and led to his long-term support of the Orangutan Foundation, a UK charity, of which he is a Trustee.
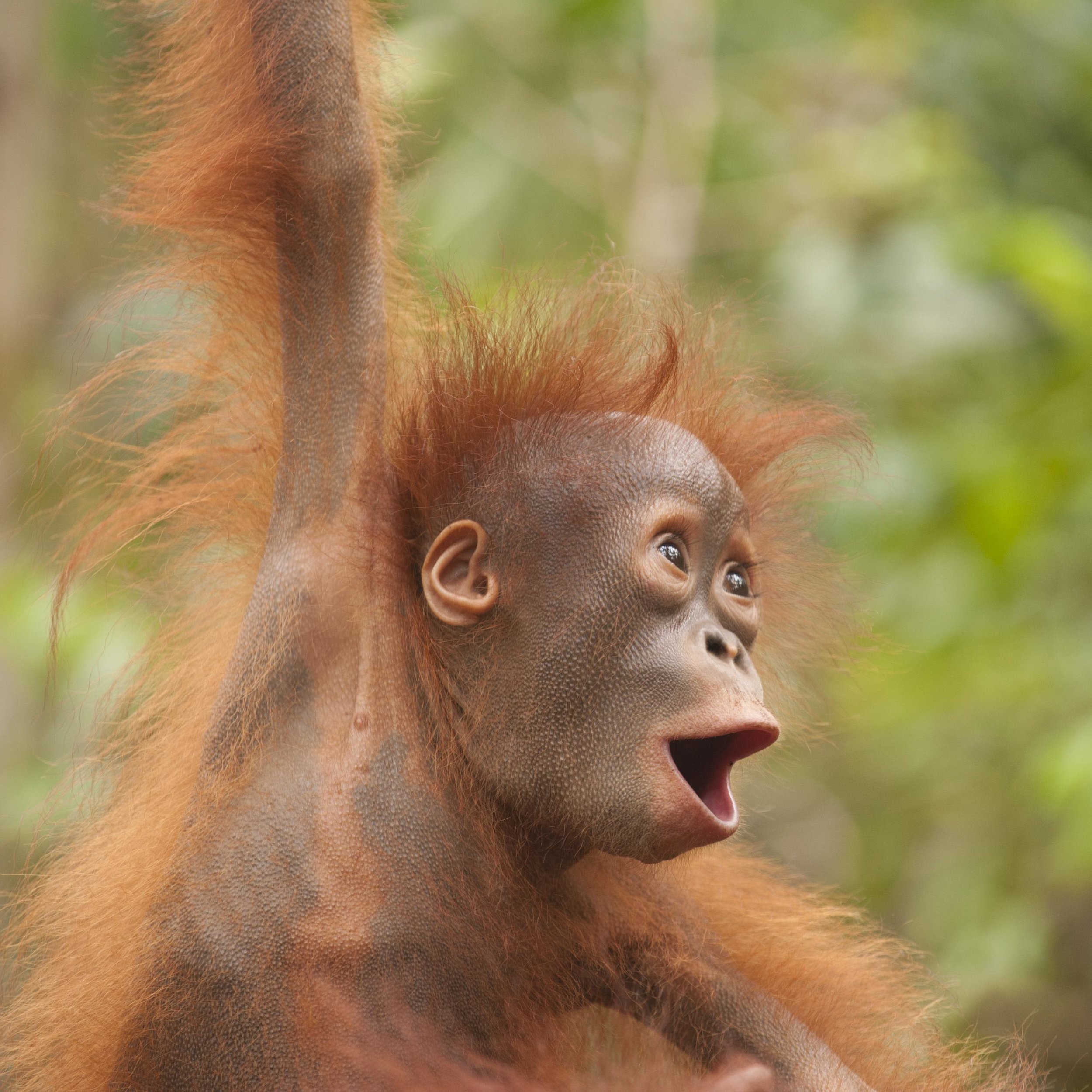

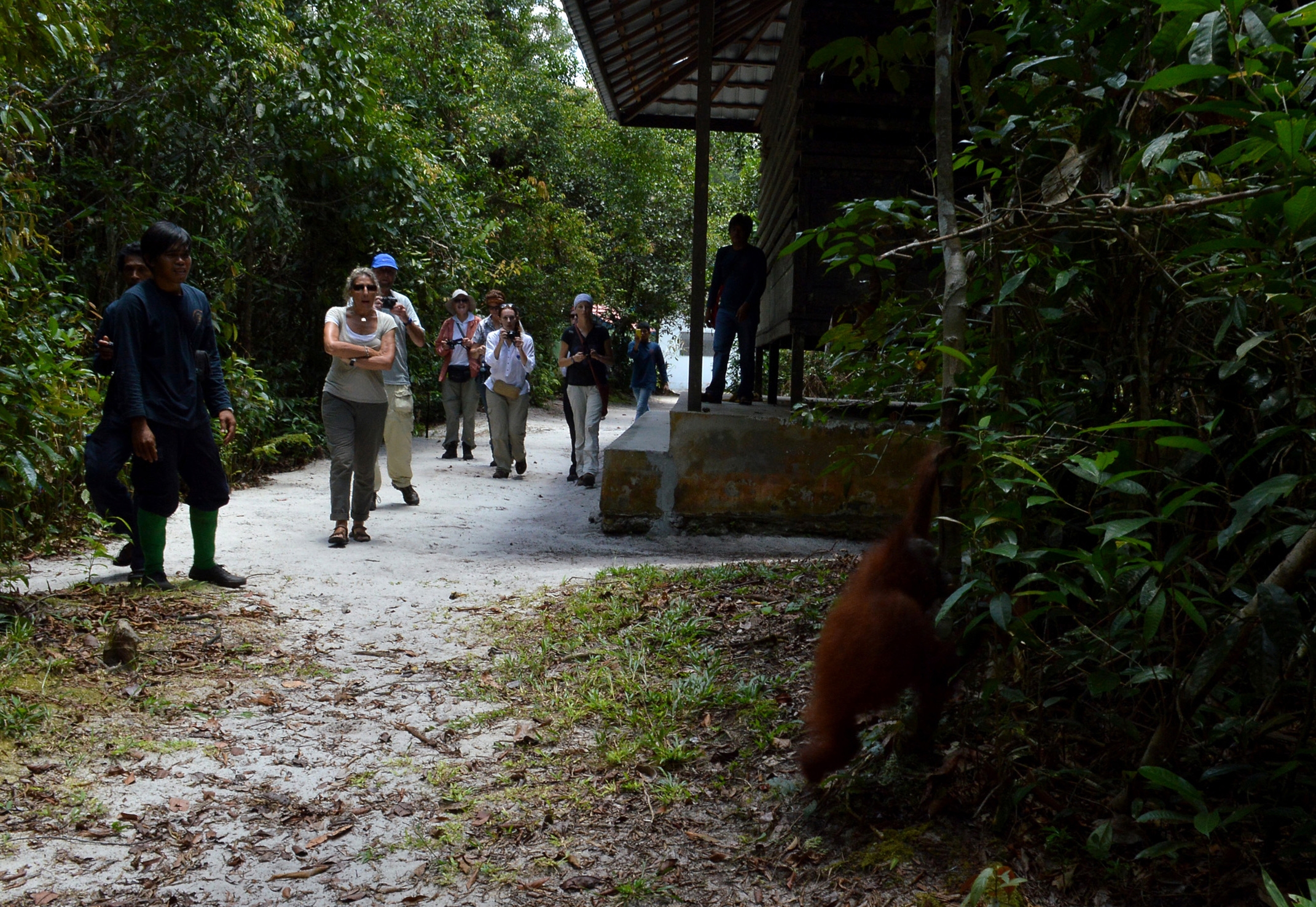
Whilst filming Terry Pratchett Facing Extinction last year, Ashley Leiman OBE, the Orangutan Foundation’s Director, invited Terry and the film crew to accompany the charity’s vet and rescue team to a proposed oil palm plantation, where an adult male orangutan was reported to be crop-raiding. The devastating threat of oil-palm plantation expansion to the endangered orangutan’s habitat required little explanation.
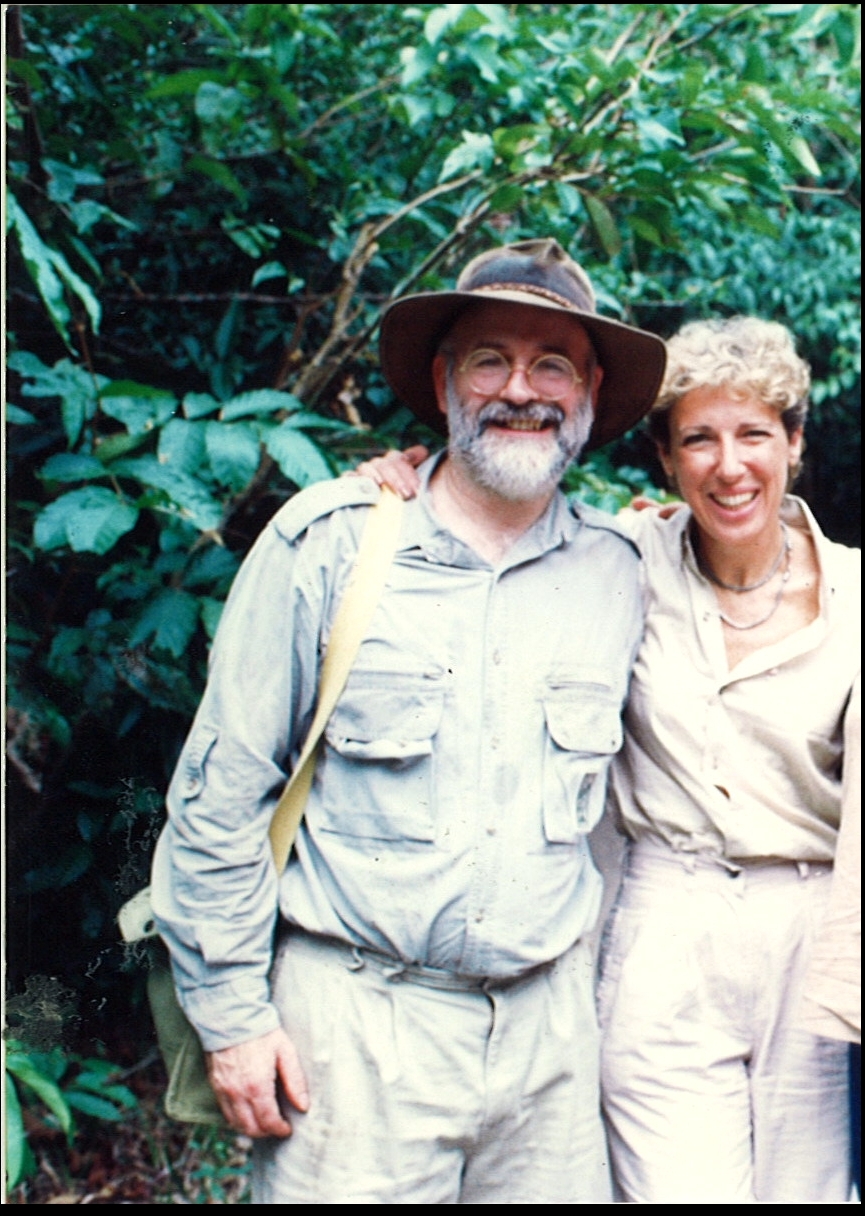

Ashley, who was also on Terry’s first adventure to Borneo, recounted “Back then, the chainsaw was our enemy. This time, we were confronted with the real threat: oil-palm plantations had replaced swathes of forest – the orangutans’ home. We drove for more than three hours through unrelenting monoculture. There was nothing but oil palm”.
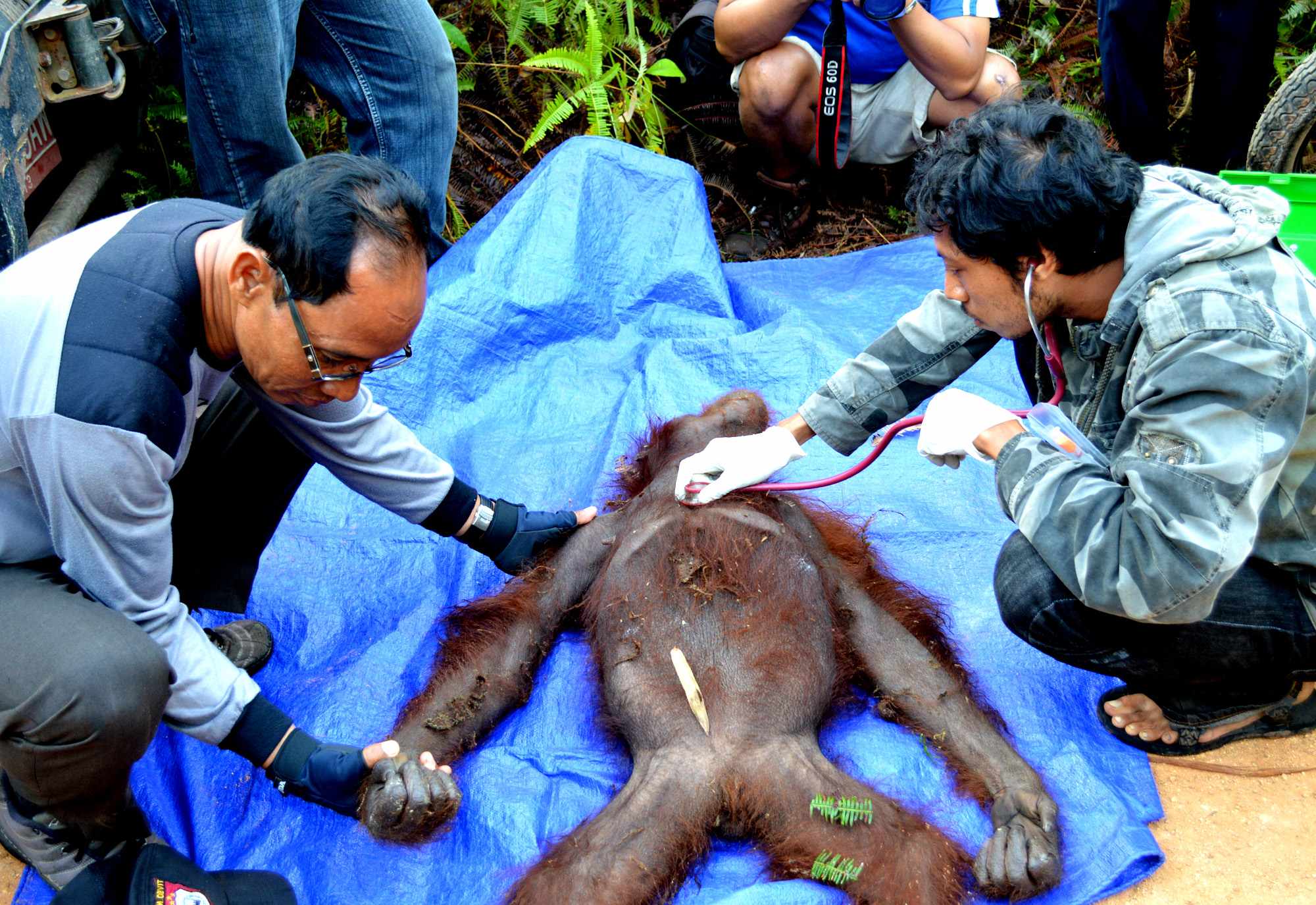
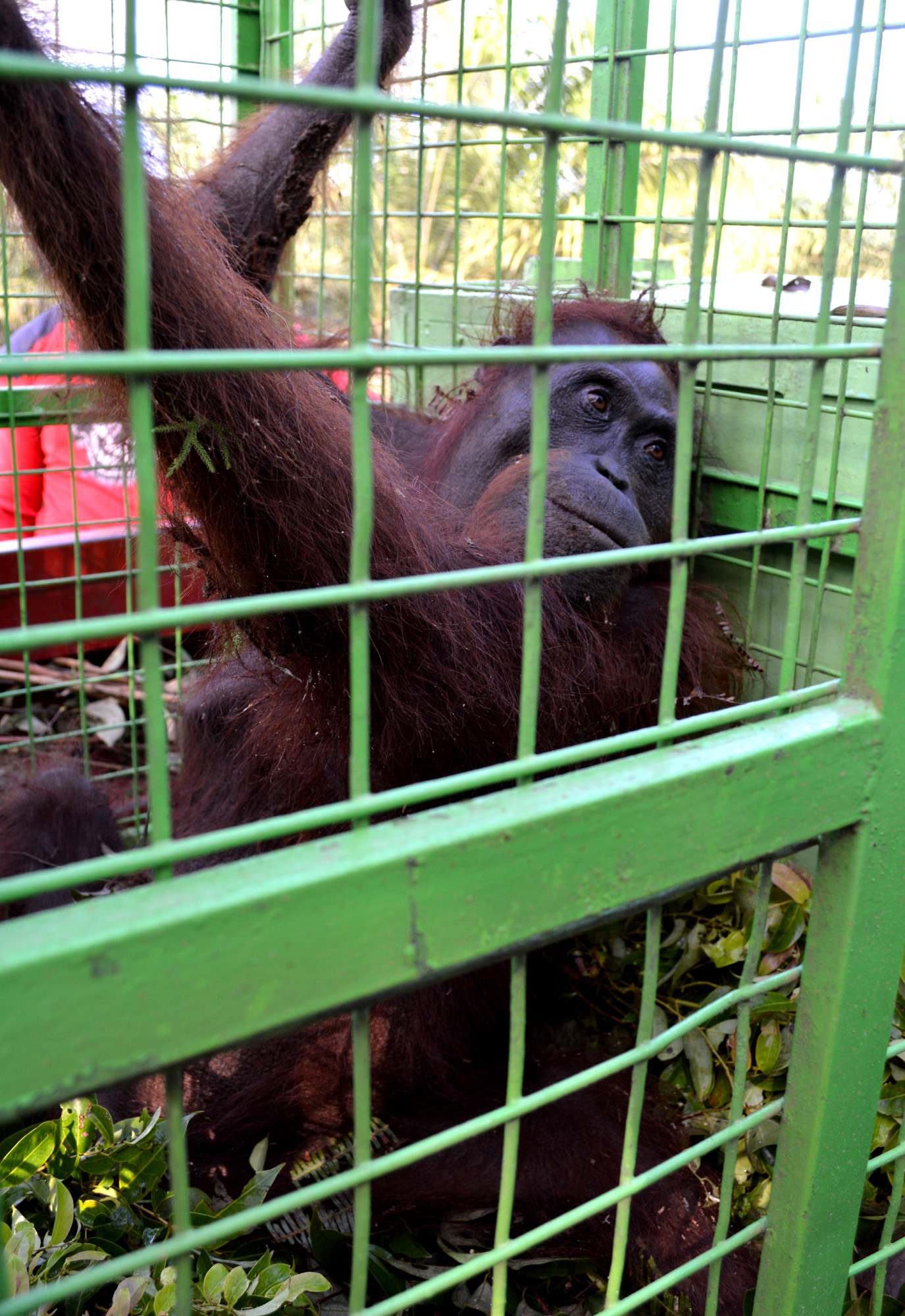
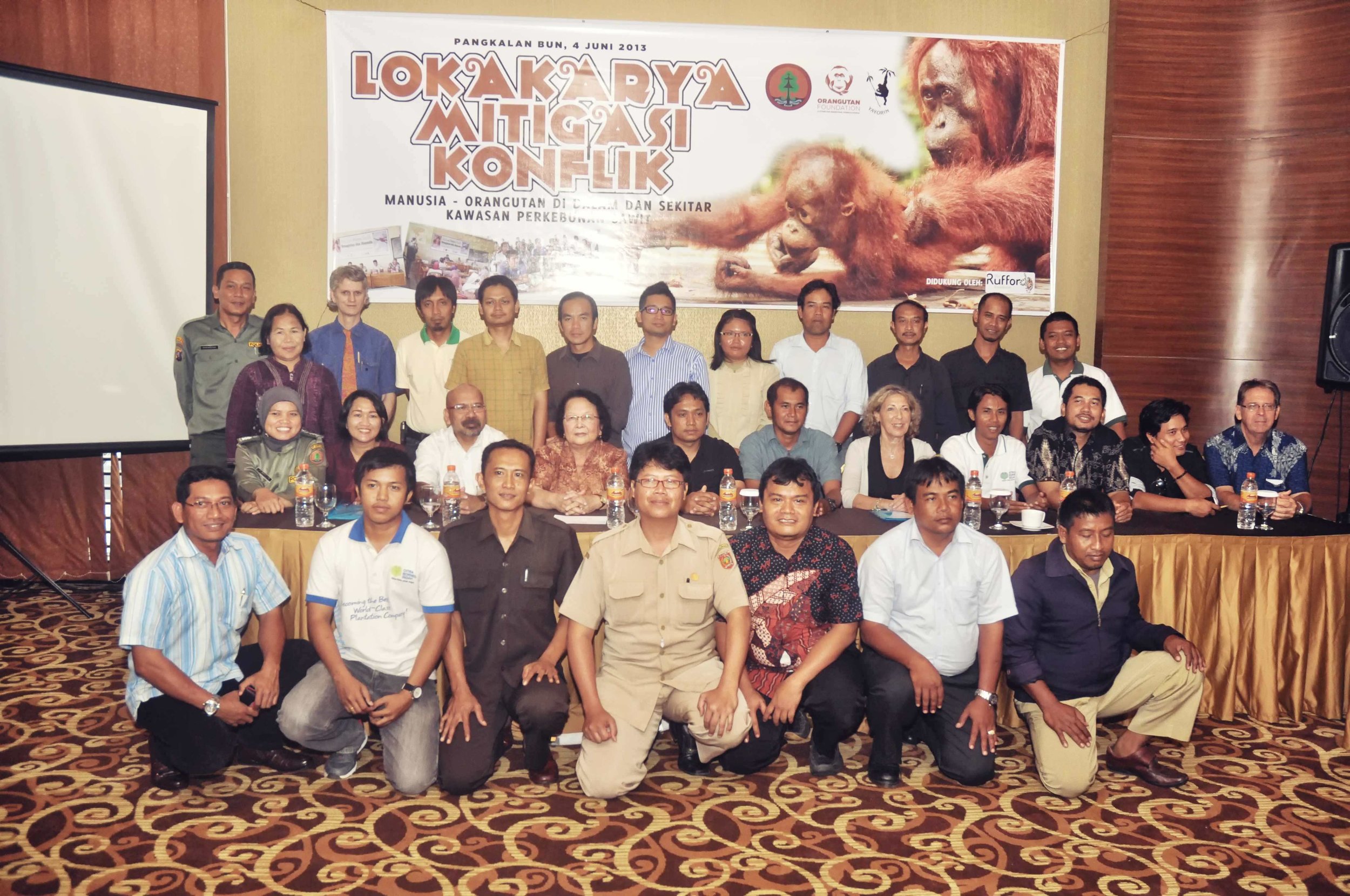
The Orangutan Foundation increasingly has to rescue stranded or injured orangutans. Only last year, a female orangutan, considered a pest, was shot over 100 times. She miraculously survived but was left permanently blind and will never return to the wild. To address this escalating issue the charity is working on a new project Mitigation of Human-Orangutan Conflicts in Central Kalimantan, Indonesian Borneo which is bringing together local government, oil palm growers and farmers to find a solution.
The Orangutan Foundation’s Director Ashley Leiman is positive about the future for orangutans “I felt privileged to be part of Terry’s latest film but I recognise that when faced with the stark reality of the situation, stranded orangutans and such forest loss, it can be hard to remain positive. Yet Terry visited some local communities who, with our assistance, are finding alternative ways to generate an income without having to destroy the forest. There is active local support for conservation in Borneo but as we know it only takes the actions of a few to undo the good work. I hope Terry recognises that his generous support over the past years has made a difference and that all is not lost.”
For more information or for interviews, please call Ian Redmond, Orangutan Foundation Trustee, on 01453 765228 or email ele@globalnet.co.uk or info@orangutan.org.uk
Notes to Editors:
High resolution photos and additional images are available here: http://bit.ly/XB5iyE
Further details about the Orangutan Foundation its activities are available on the Foundation’s website www.orangutan.org.uk
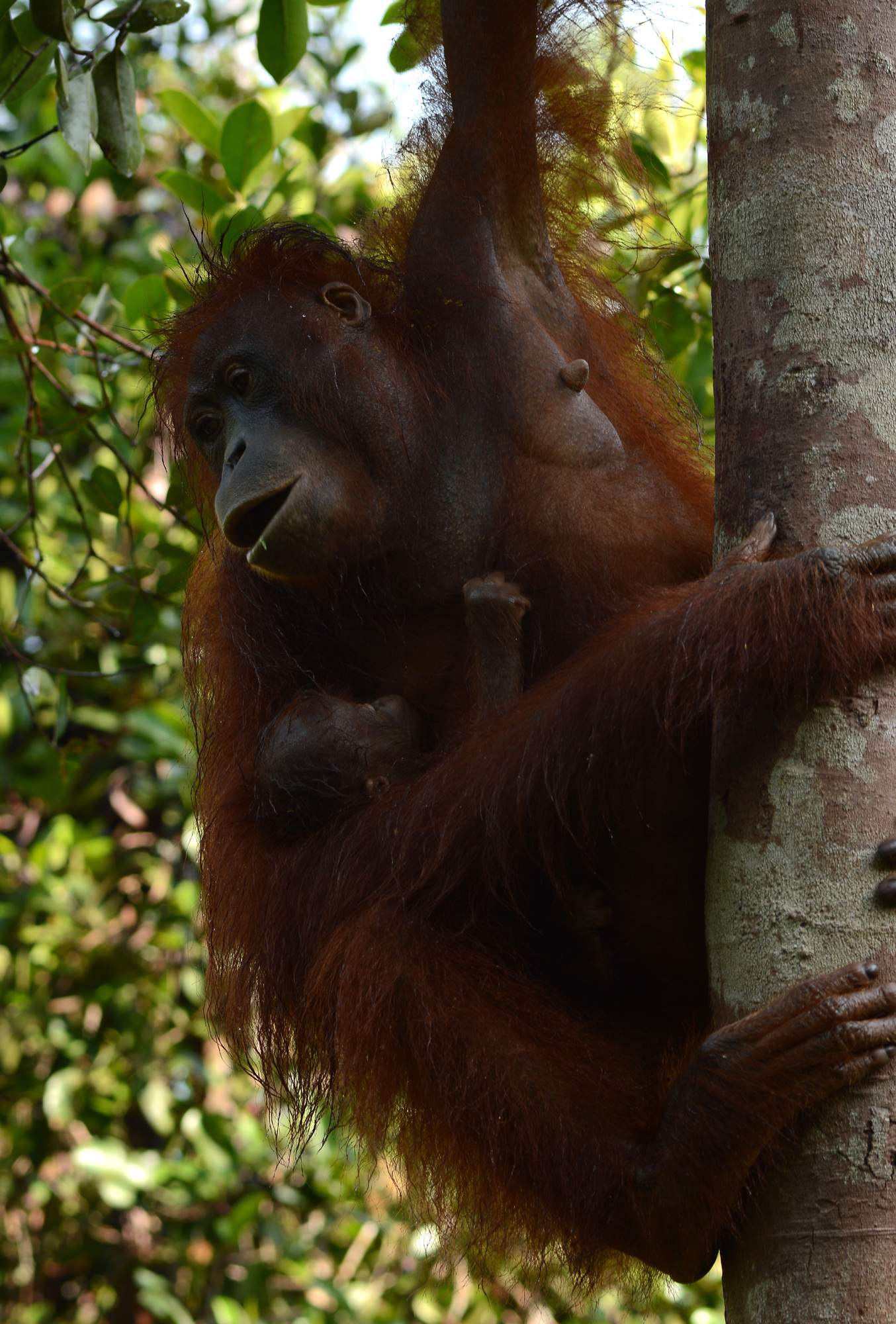
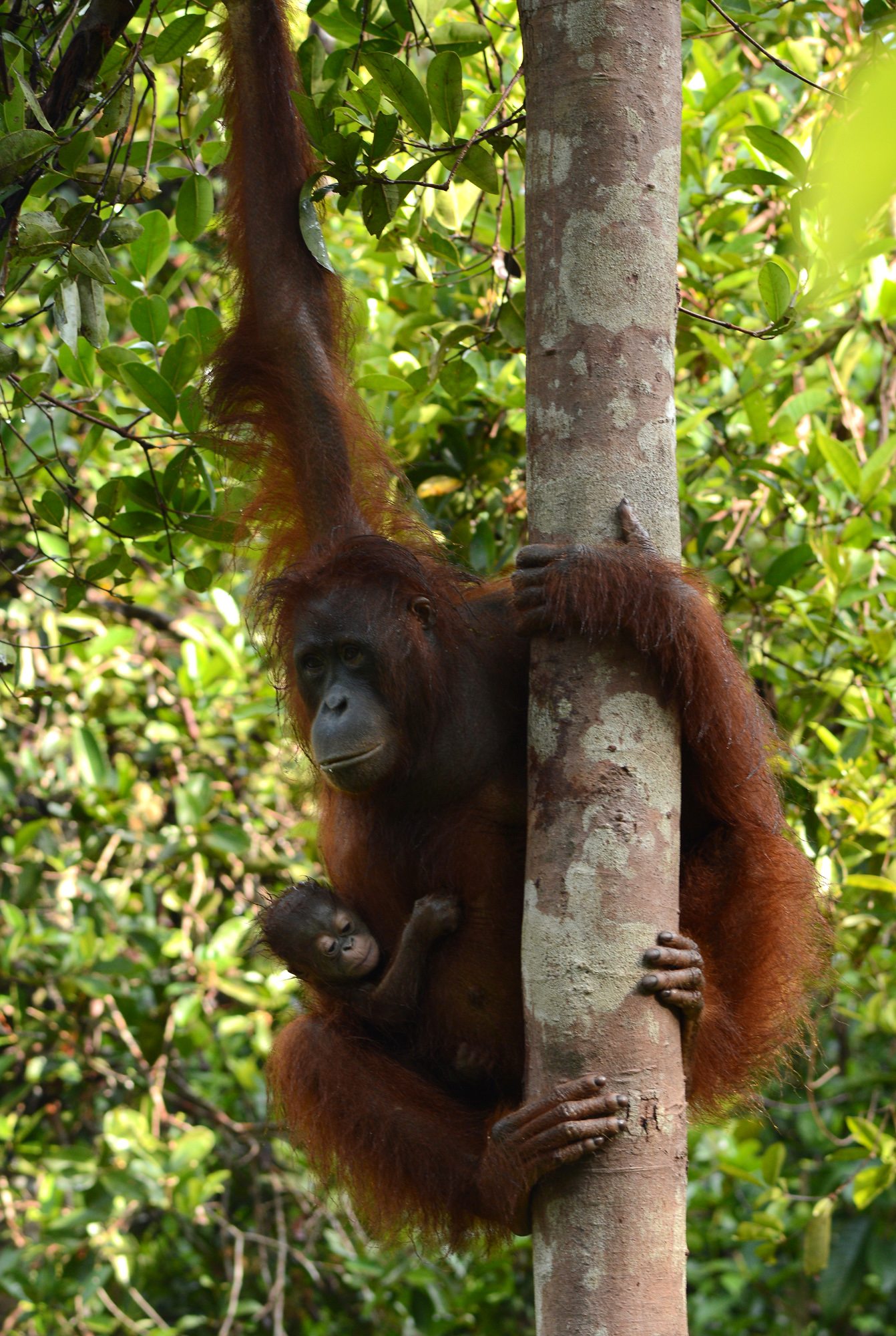
The Orangutan Foundation works in Indonesian Borneo and Sumatra to protect endangered orangutans by protecting their tropical forest habitat, working with local communities and promoting research and education. It recognises that orangutan habitat is unique in its richness of biodiversity and is crucial for local communities, who are as dependant on the forest as is the orangutan.
The Orangutan Foundation work in areas of critical orangutan habitat in Central Kalimantan, in the Indonesia part of Borneo. Additionally, In collaboration with the Indonesian government’s local Nature Conservation department (PHKA), the Orangutan Foundation runs a release site for rehabilitated and translocated wild orangutans in the Lamandau River Wildlife Reserve.
Sir Terry Pratchett, Trustee of the Orangutan Foundation, is one of the most popular authors writing today. He is best known for his hugely popular Discworld novels, a fantasy series, which feature the Discworld character The Librarian, who was transformed into an orangutan. This prompted Terry Pratchett’s curiosity about orangutans and his long-term support of the Orangutan Foundation. In 1995 Terry visited Indonesian Borneo with Orangutan Foundation to see orangutans in the wild and film Terry Pratchett’s Jungle Quest for a Channel 4 television documentary and he returned in 2012 to film Terry Pratchett Facing Extinction for BBC2. Terry has won numerous literary awards, has received four honorary doctorates, was appointed OBE for services to literature in 1998 and he was knighted in the 2009 New Year Honours.
Ms Ashley Leiman OBE is Director and Trustee of the Orangutan Foundation, which she founded in 1990. Ashley has been actively involved in Asian conservation for over 30 years. Her initial involvement was with the Natural History Society and Conservation Society in Hong Kong. In 1985 she was on the organising committee of the New York Rainforest Alliance. In 1986, after spending time in Tanjung Puting National Park, Indonesian Borneo, Ashley set about establishing the Orangutan Foundation in the UK. In 2006 Ashley was appointed OBE for her services to Orangutan Conservation. Ashley is also a member of the Executive Committee of the UNEP’s Great Apes Survival Project (GRASP).
Threats to orangutans
The biggest threat to orangutans is habitat loss. Orangutan habitat is being destroyed and degraded by oil palm plantations, illegal logging, acacia plantations, fire, mining and small-scale shifting cultivation.
The destruction of tropical forests affects the global climate and is one of the world’s most pressing environmental concerns. For orangutans the situation is critical.
The principle cause of habitat loss is the conversion of forests to agriculture, especially vast monoculture oil palm plantations.
Palm oil is produced from the kernel of the oil palm plant and is the world’s most popular vegetable oil, primarily produced in Indonesia and Malaysia. Often labelled as just vegetable oil, palm oil is a hidden ingredient found in up to half of packaged food products across Europe, it is also used in cosmetics and increasingly as a biofuel. A new EU regulation, requiring all vegetable oils to be labelled individually, will come into force in 2015.
Oil palm plantations expansion is not the only threat. Deforestation for mining (both legal and illegal) has the potential to be just as devastating. Illegal mining has been found within the boundaries of the Lamandau River Wildlife Reserve. The Orangutan Foundation is protecting this area of critical orangutan habitat with guard posts and patrols.
Images – high resolution versions can be downloaded from the Orangutan Foundation Photo Gallery from this link http://bit.ly/XB5iyE
To donate to the Orangutan Foundation please click here or text APES05 £X to 70070 and put whatever amount you would like to donate where the 'X' is. For example, to donate £20, text APES05 £20. Thank you!
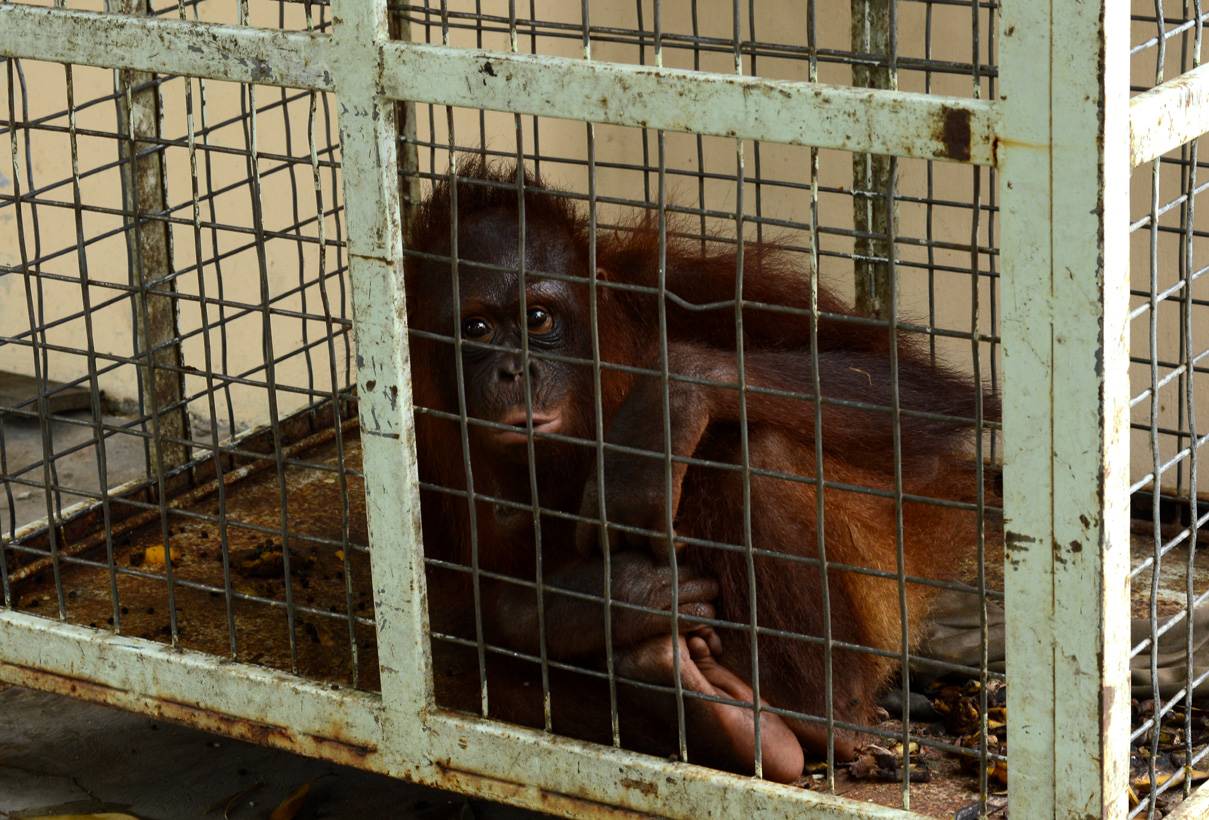
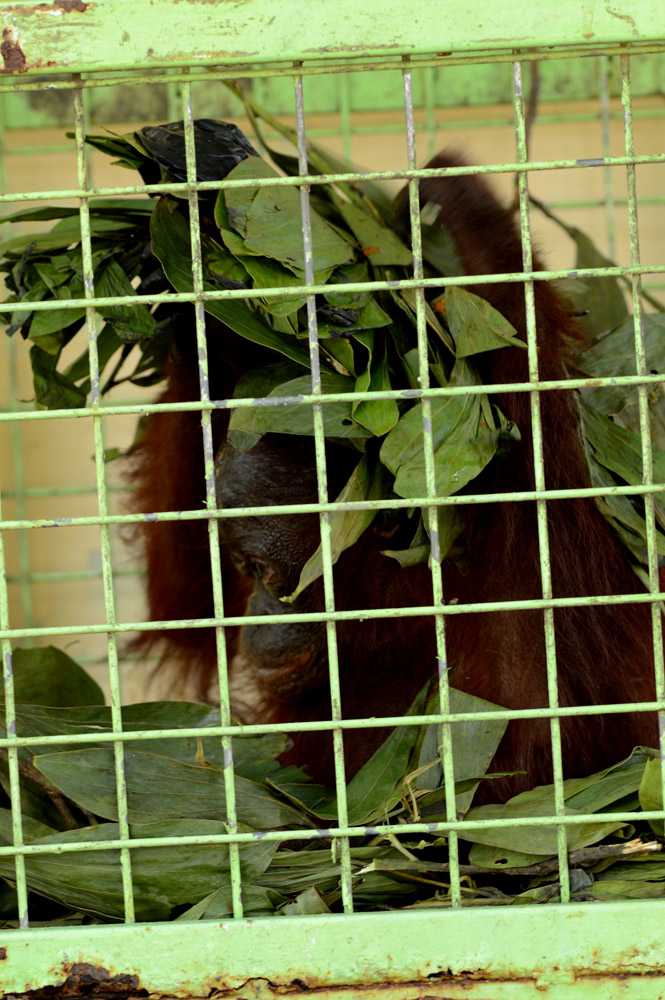
 The Foundation is always asked 'How is the situation - facing the orangutans?'. We answer 'The Foundation is making progress', in one way by working closely with villagers and oil palm companies to mitigate human-wildlife conflict'. This strategy is working, as the Foundation is called upon to rescue stranded orangutans, rather than the individuals being harmed. Within one week in April, the Field staff were called upon to translocate four orangutans that had entered villager's farm land. One orangutan was found in a chicken farm and had eaten bananas and coconuts from the orchard on her way! These situations must be extremely frustrating for the farmers and yet rather than injure the marauding orangutan, the local people now know that there is an alternative, and that is to call upon the Rescue Team (OF and BKSDA).
The Foundation is always asked 'How is the situation - facing the orangutans?'. We answer 'The Foundation is making progress', in one way by working closely with villagers and oil palm companies to mitigate human-wildlife conflict'. This strategy is working, as the Foundation is called upon to rescue stranded orangutans, rather than the individuals being harmed. Within one week in April, the Field staff were called upon to translocate four orangutans that had entered villager's farm land. One orangutan was found in a chicken farm and had eaten bananas and coconuts from the orchard on her way! These situations must be extremely frustrating for the farmers and yet rather than injure the marauding orangutan, the local people now know that there is an alternative, and that is to call upon the Rescue Team (OF and BKSDA).
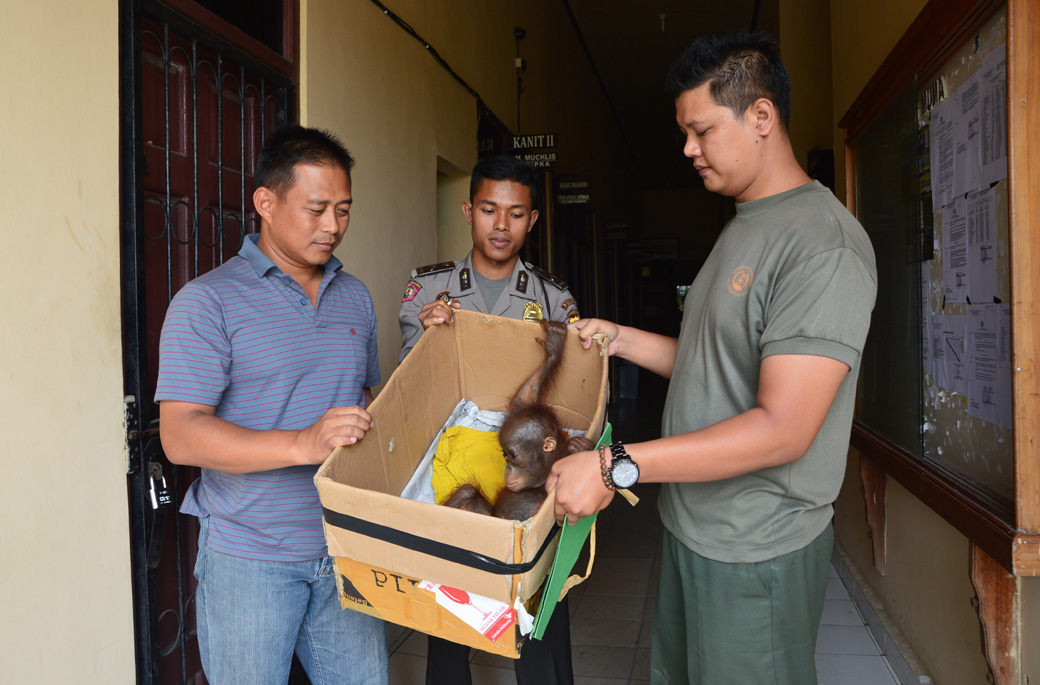
















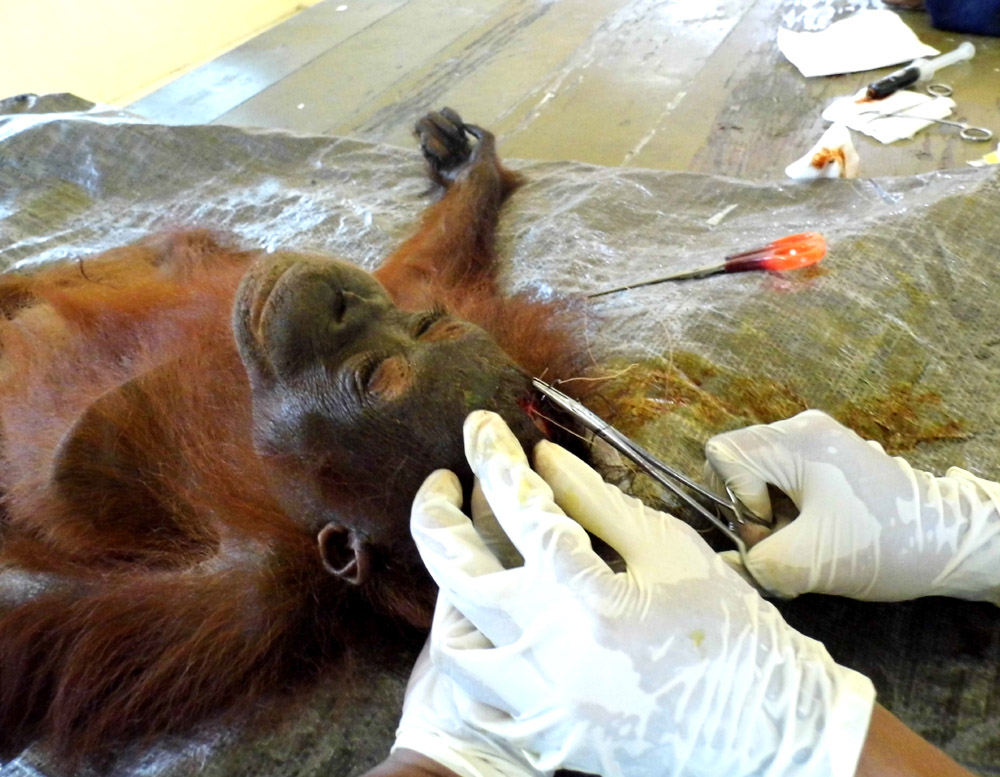
 Melan was the orangutan who we rescued back in April, who had the head wound that required our vet to stitch the skin back together over the top of the head - a tricky job! This is the sort of wound that any individual would almost certainly die from if left untreated.
Melan was the orangutan who we rescued back in April, who had the head wound that required our vet to stitch the skin back together over the top of the head - a tricky job! This is the sort of wound that any individual would almost certainly die from if left untreated.

















































