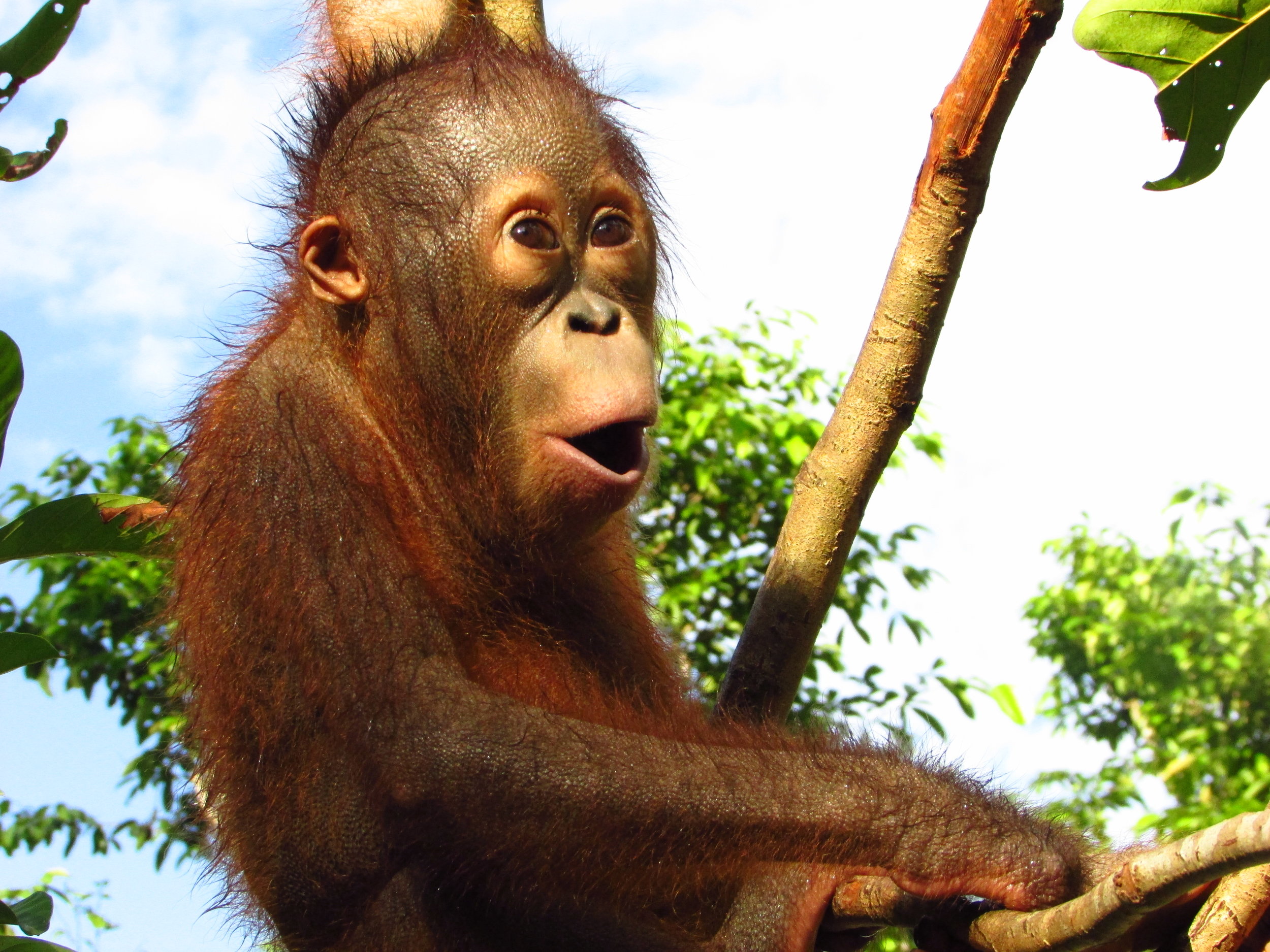
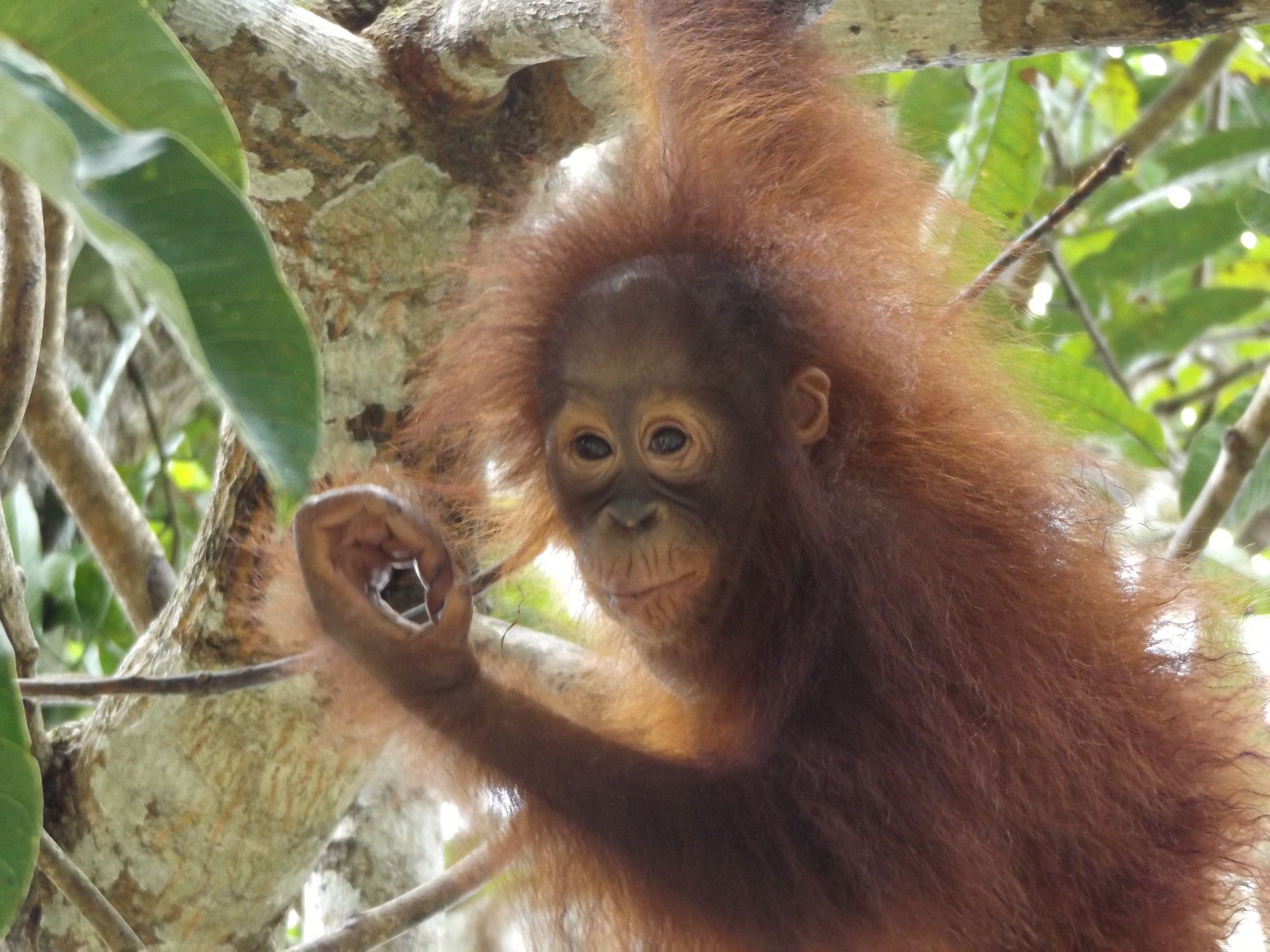
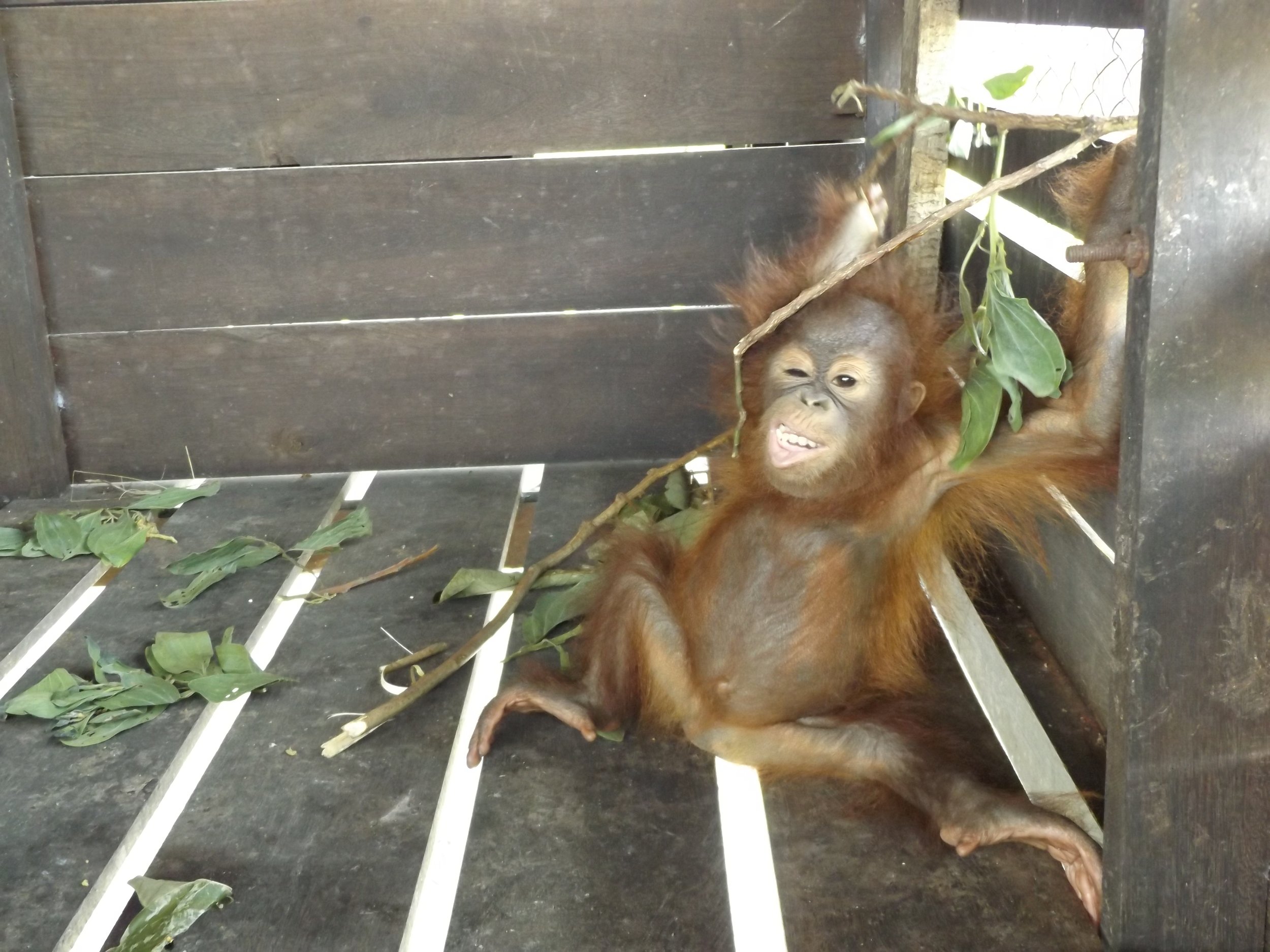
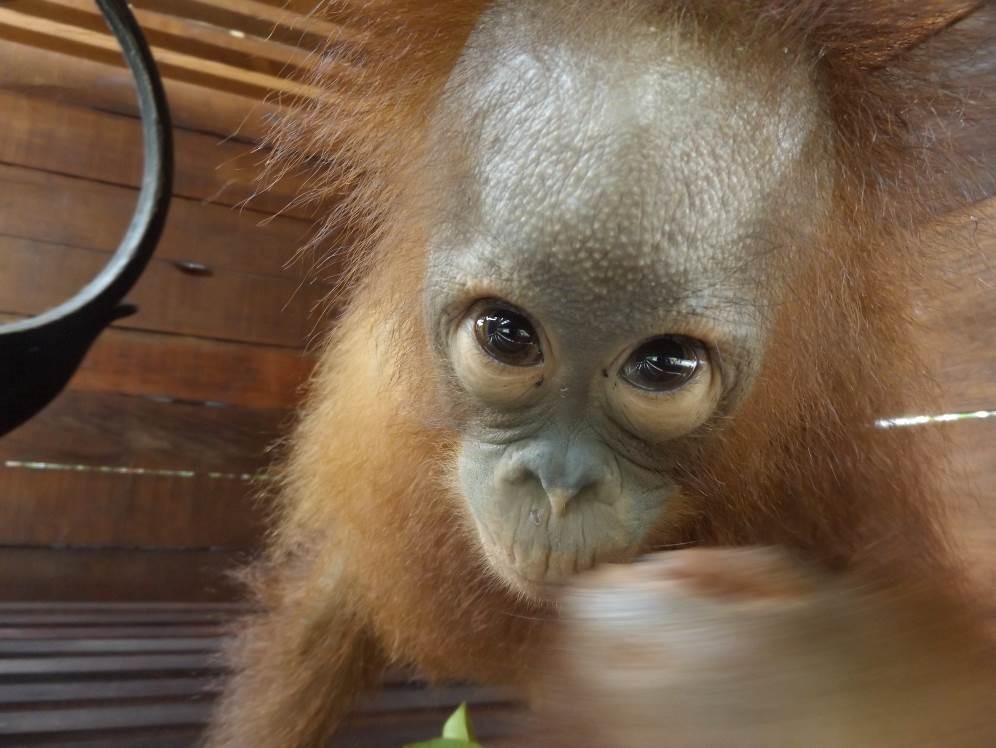
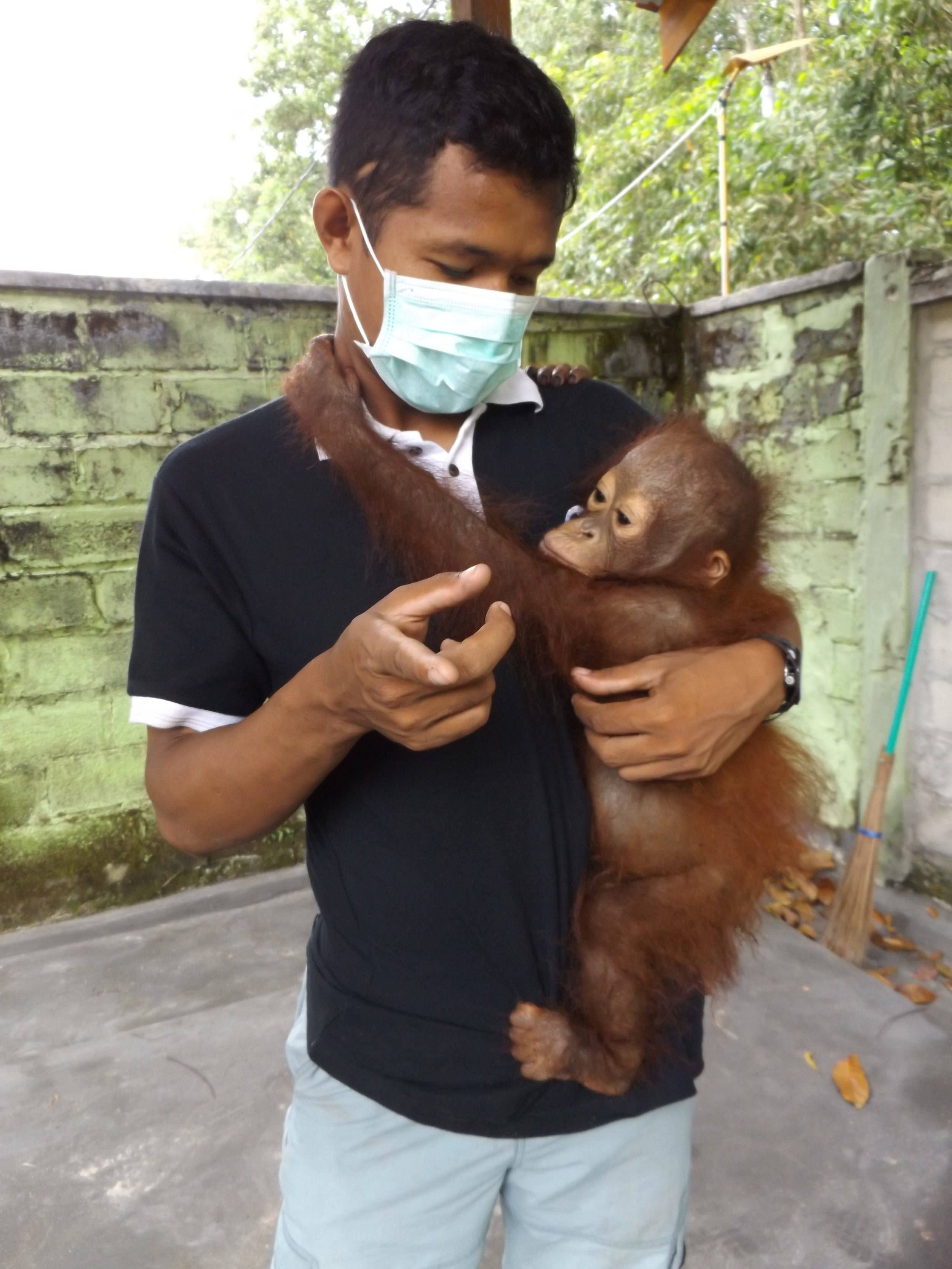
Biologically speaking, humans and orangutans are similar as we share around 97% of the same DNA. It could be said that orangutans also share comparable traits with us when it comes to parenting, as mothers teach their young essential skills for later life, and provide them with shelter each night.
As Orangutan Foundation’s founder and director/trutee, Ashley Leiman, says: “It is very special to watch a mother and infant together. I think the bond is so exceptional because orangutans are solitary. I’ve seen gorillas and chimps with offspring and the whole group is involved in the upbringing. Likewise elephants - if a calf falls over, all the aunties and extended family reach out to pick it up and get it back on its feet. With orangutans, all that care and teaching and relationship is condensed into the mother-infant bond. The mother’s eyes are never off the young”.
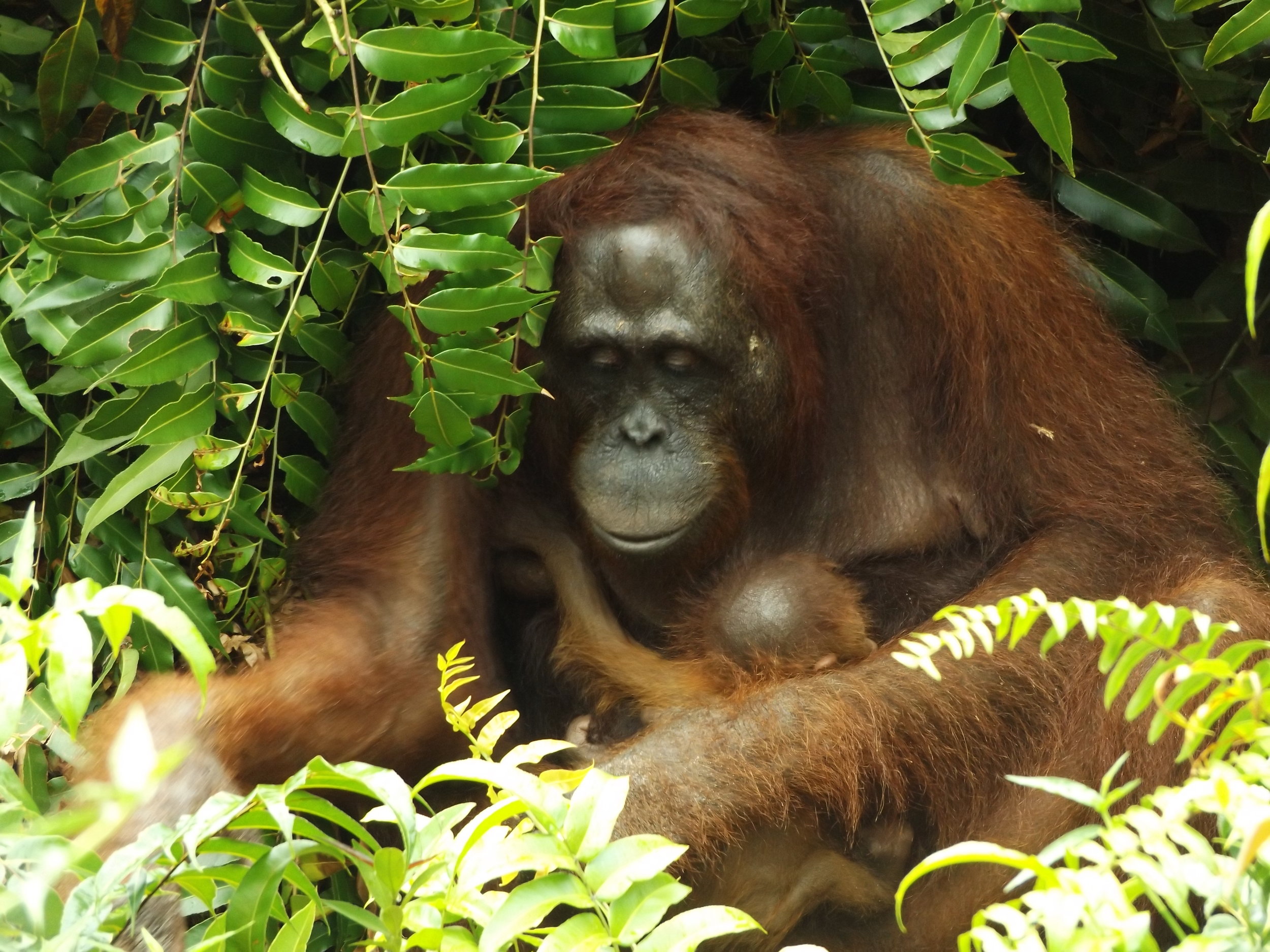
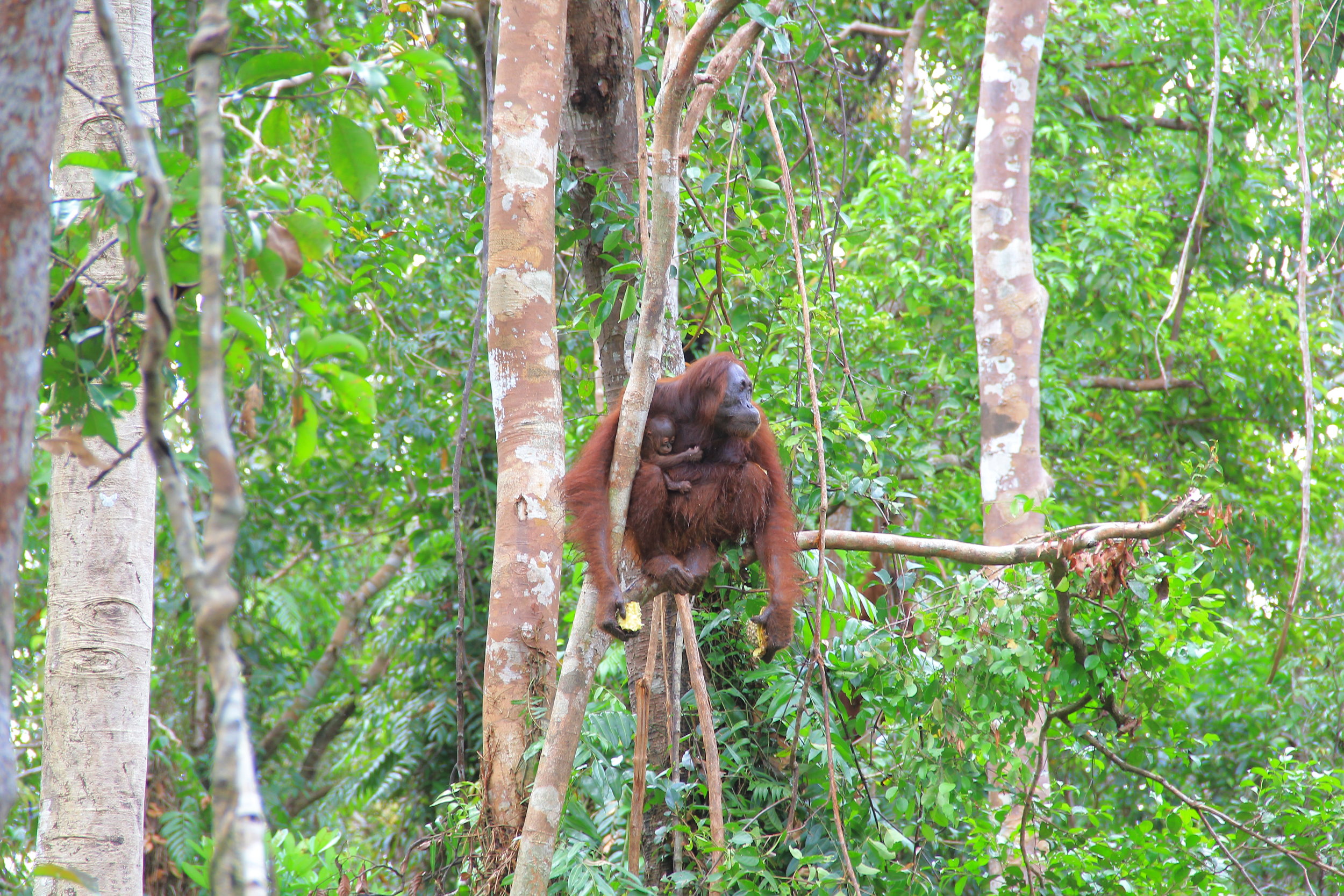
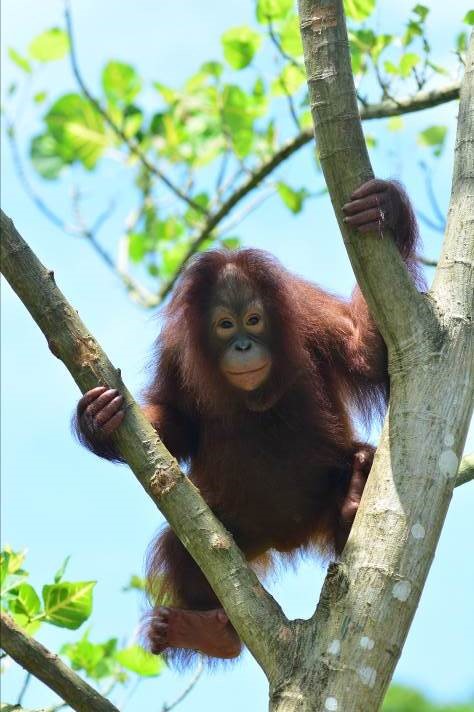
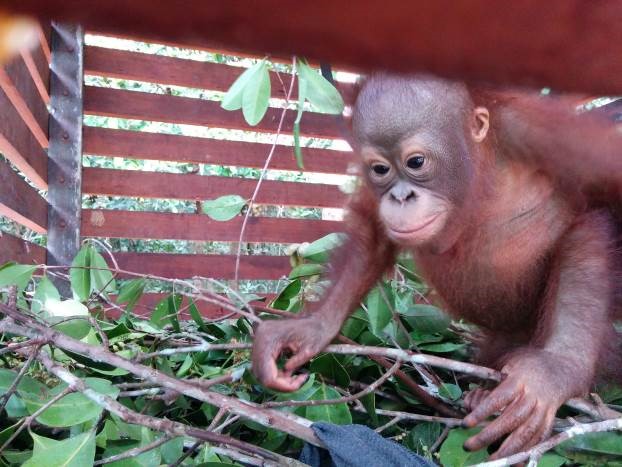
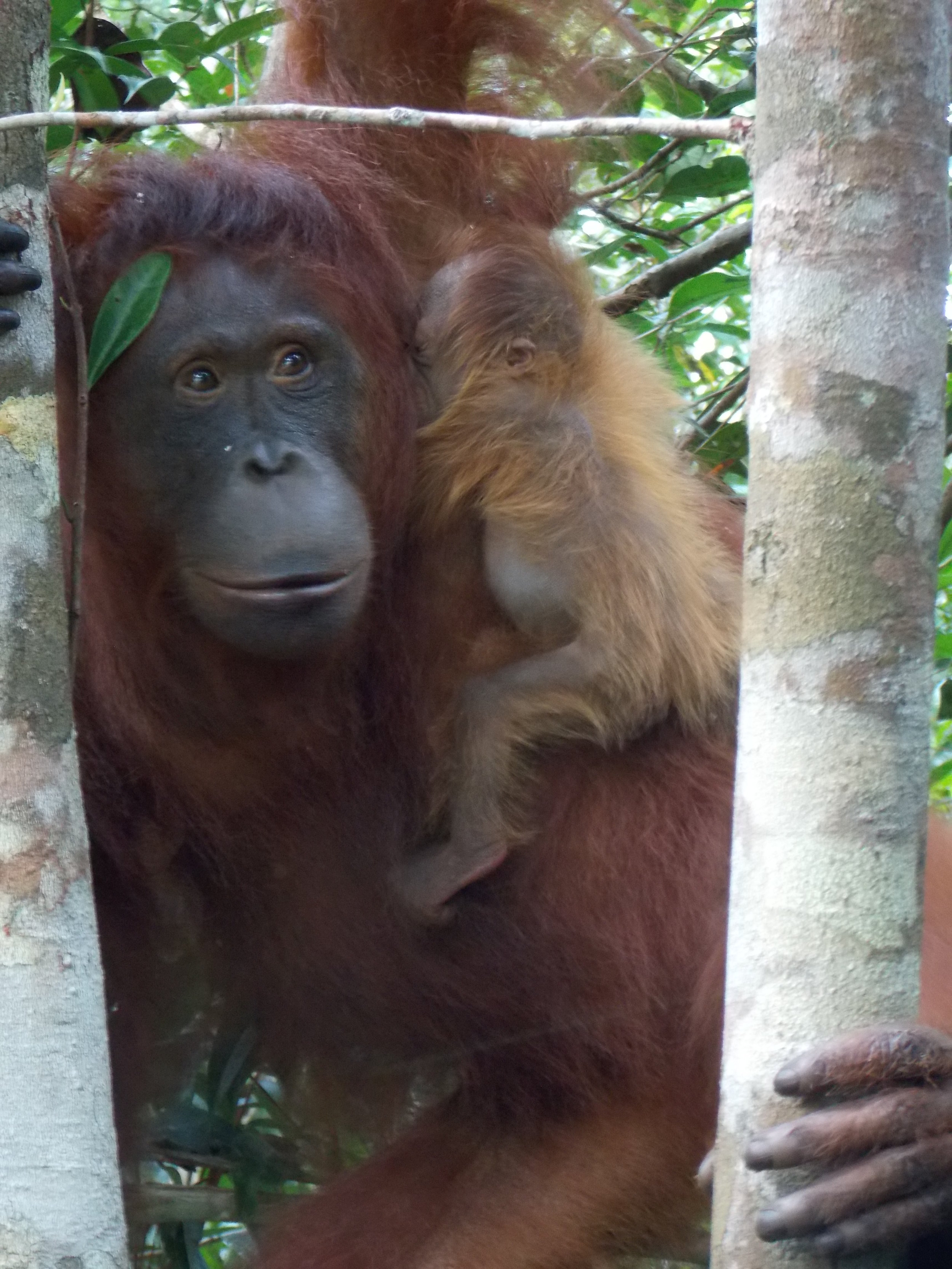
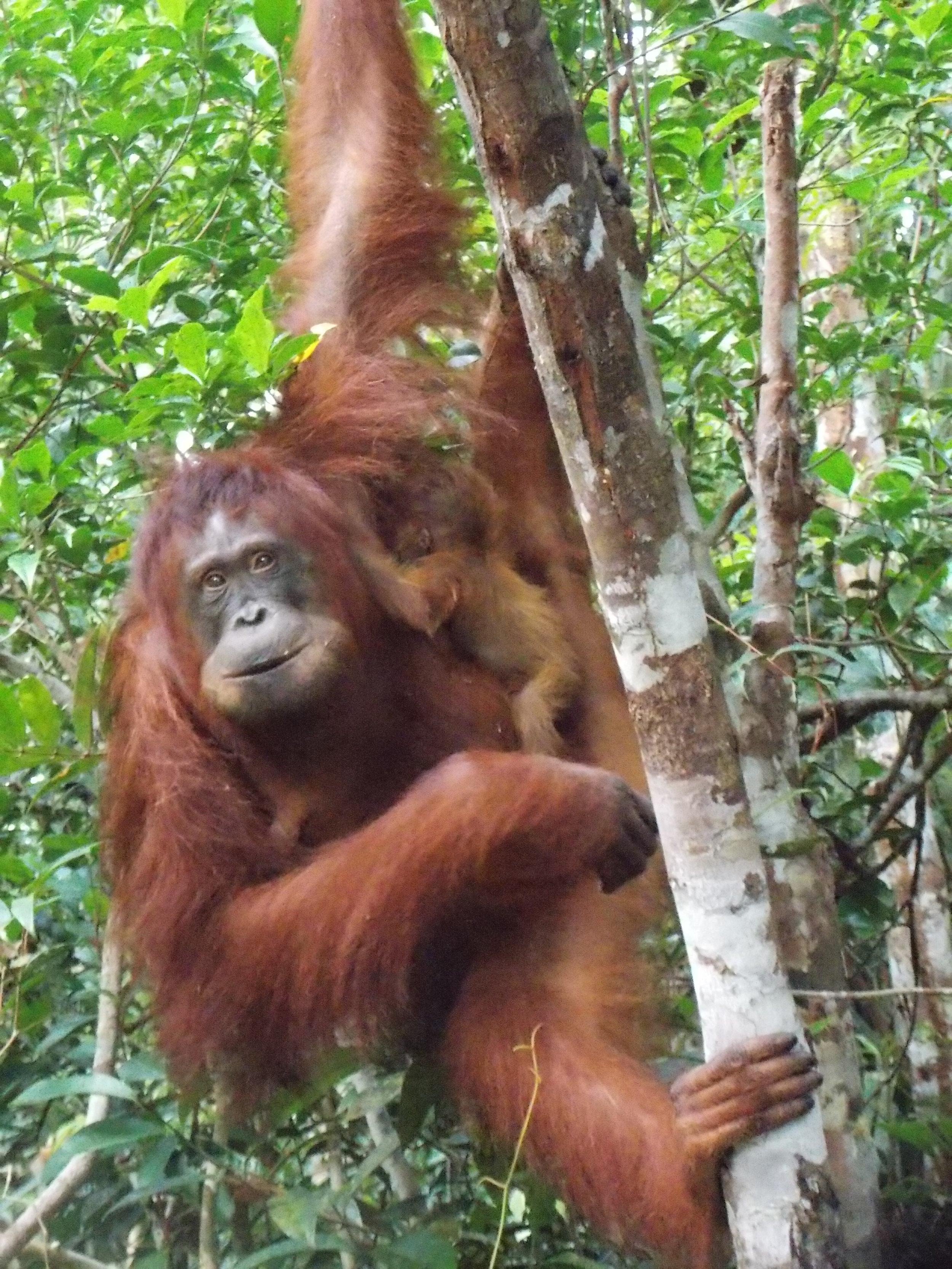
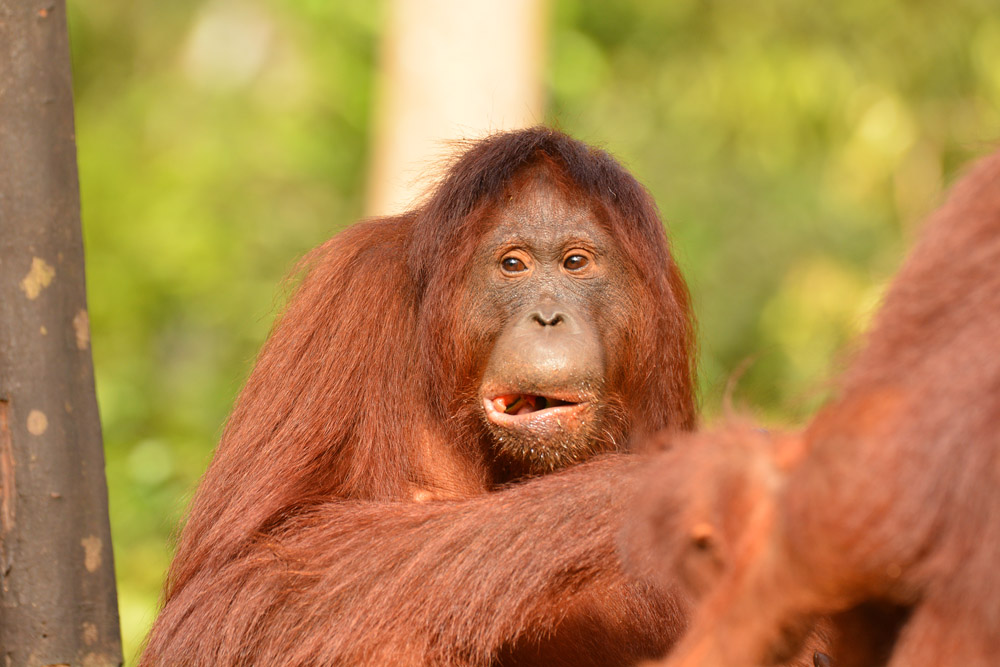
Suwita gives our team a rare glimpse of her young infant
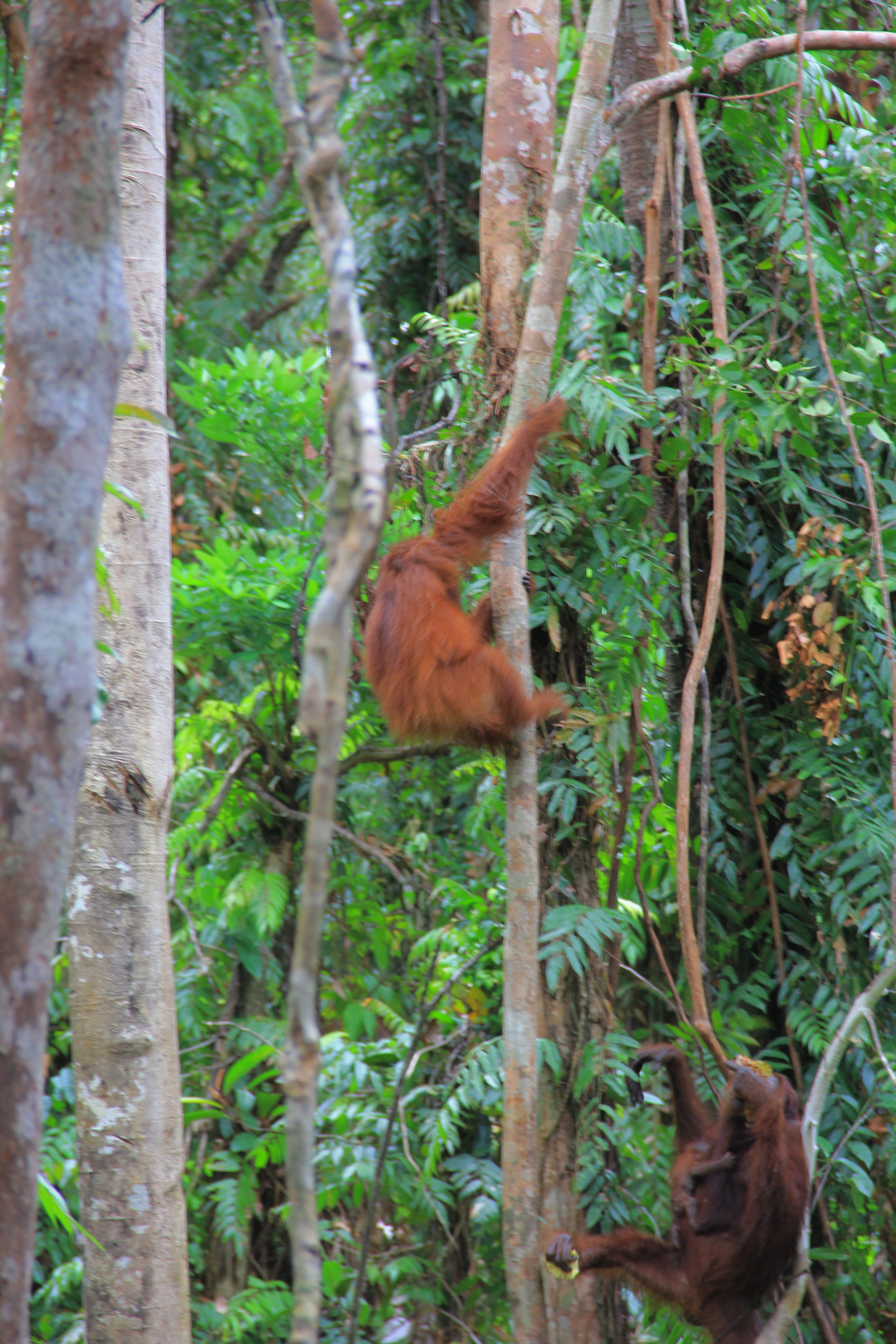
Wild female orangutan Suwita has shown these crucial maternal characteristics over the previous weeks as she carefully looks after her new baby and appears to be showing the nurturing instincts you would expect for an orangutan mother’s first offspring.
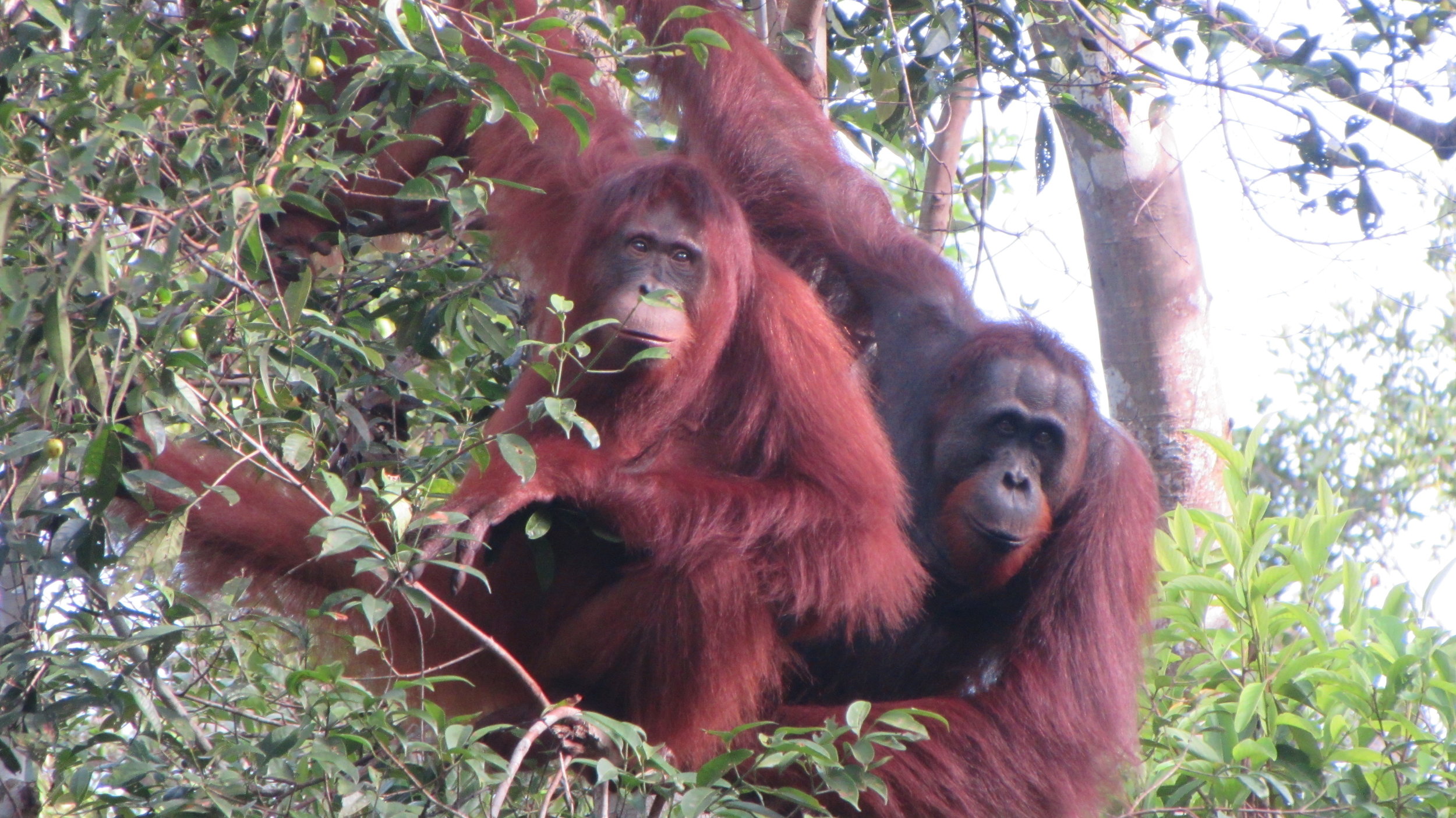
Suwita was born in the forest near Camp Rasak in 2009 and of the four new wild orangutan mothers discovered recently within the Lamandau Wildlife Reserve, Suwita looks to be the most protective of her new baby.
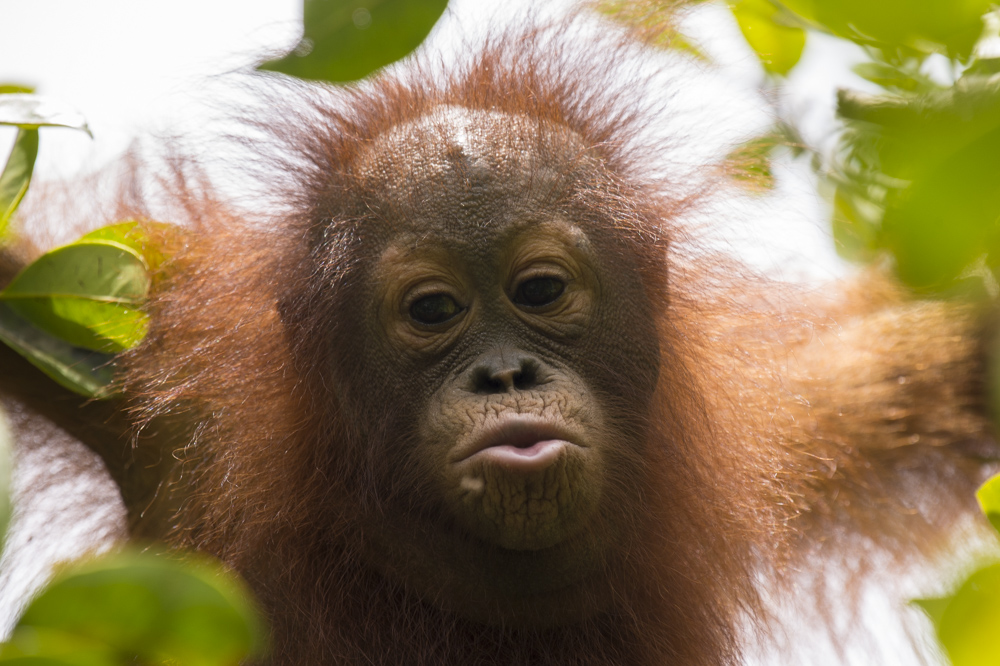
Our field teams are continuously monitoring wild and reintroduced orangutans inside this protected habitat, and to help keep a visual record of their development, we try and take photographs from a suitable distance. Following careful observations of Suwita, it has now been discovered that her offspring is in fact male and has been given the name Samuel, but it hasn’t been easy to get a clear sight of the young primate.
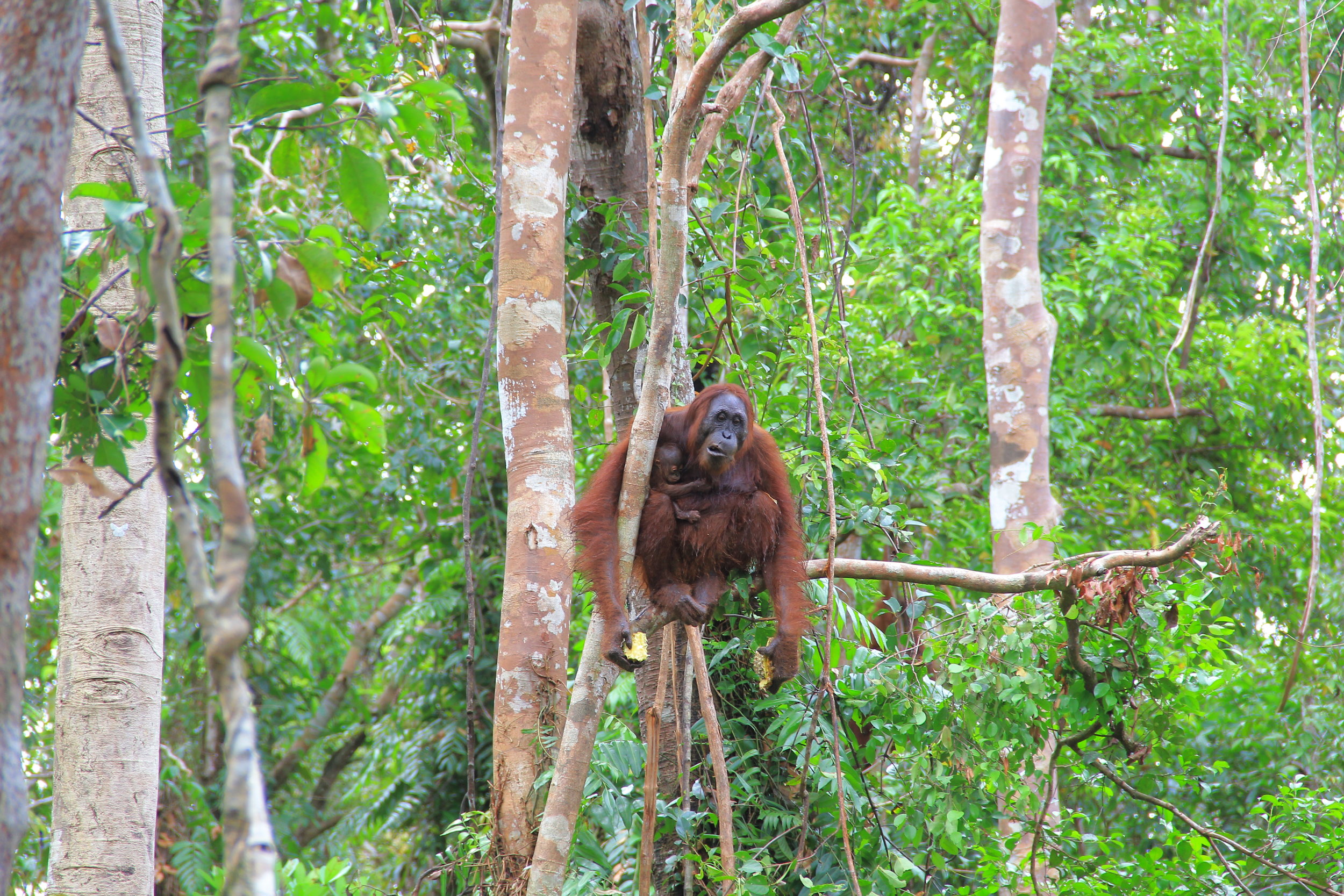
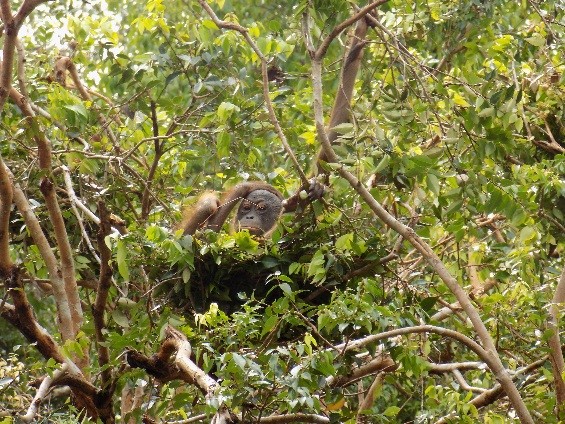
Young Samuel is kept close as his mother feeds
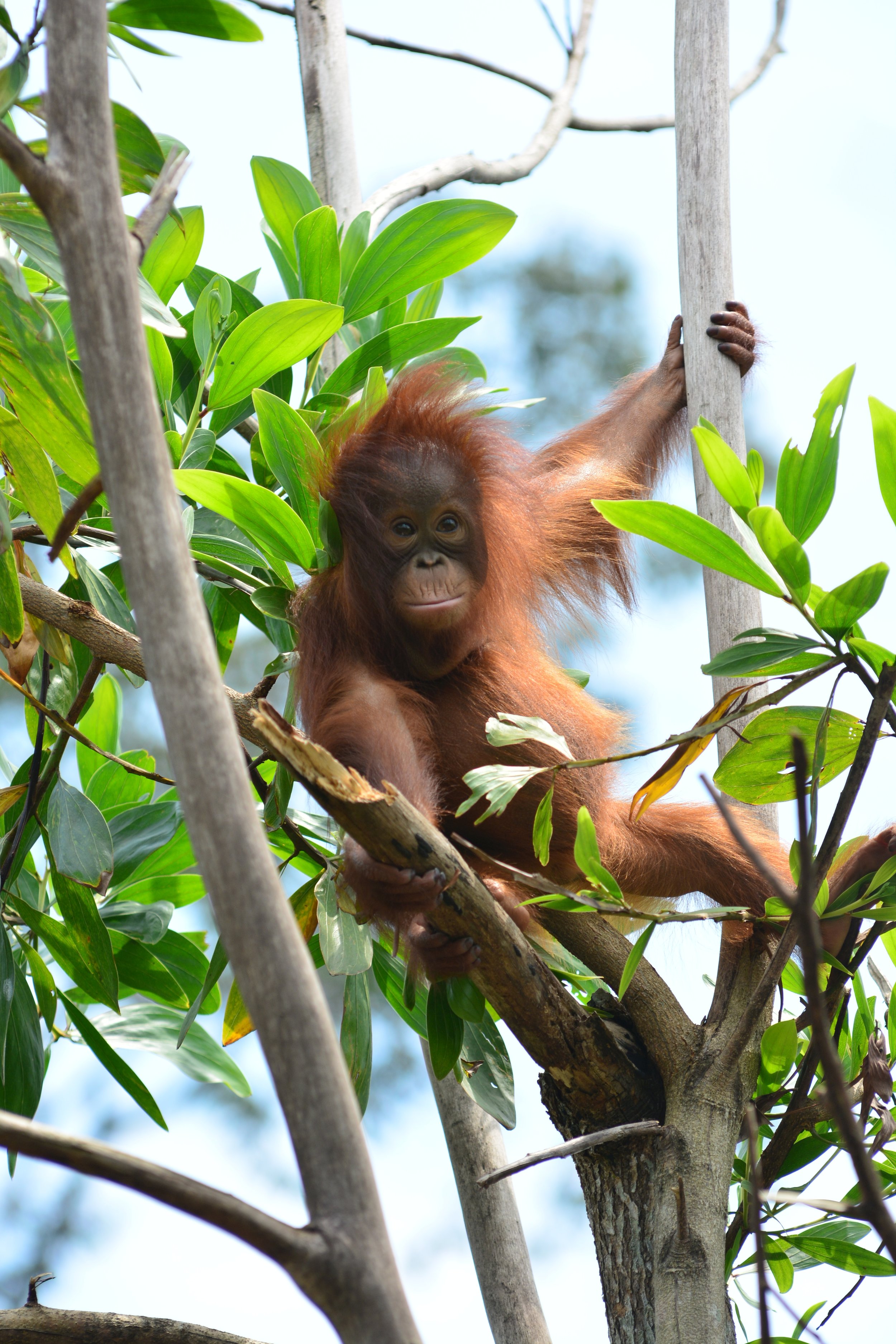
Unlike the other recent orangutan mothers who almost appear to show off their newborns, Suwita is very protective to the extent that our team initially struggled somewhat in identifying the sex of her infant. When sat on a branch in trees Suwita rests her son securely on her lap to feed, and when travelling through the canopy she always makes sure that Samuel is safe and holding on tight, away from prying eyes.
Suwita is proving to be a doting mother to Samuel. It’s quite possible that her protective nature has developed from memories of her mother Sawit, but whatever the reason, it’s wonderful for us to observe a wild orangutan so caring for her first offspring.
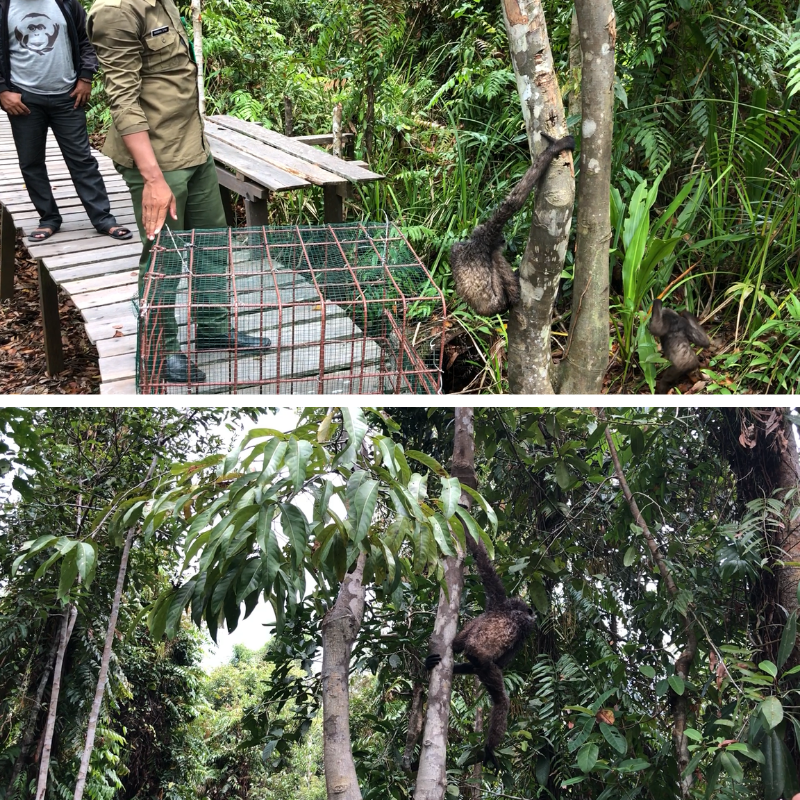
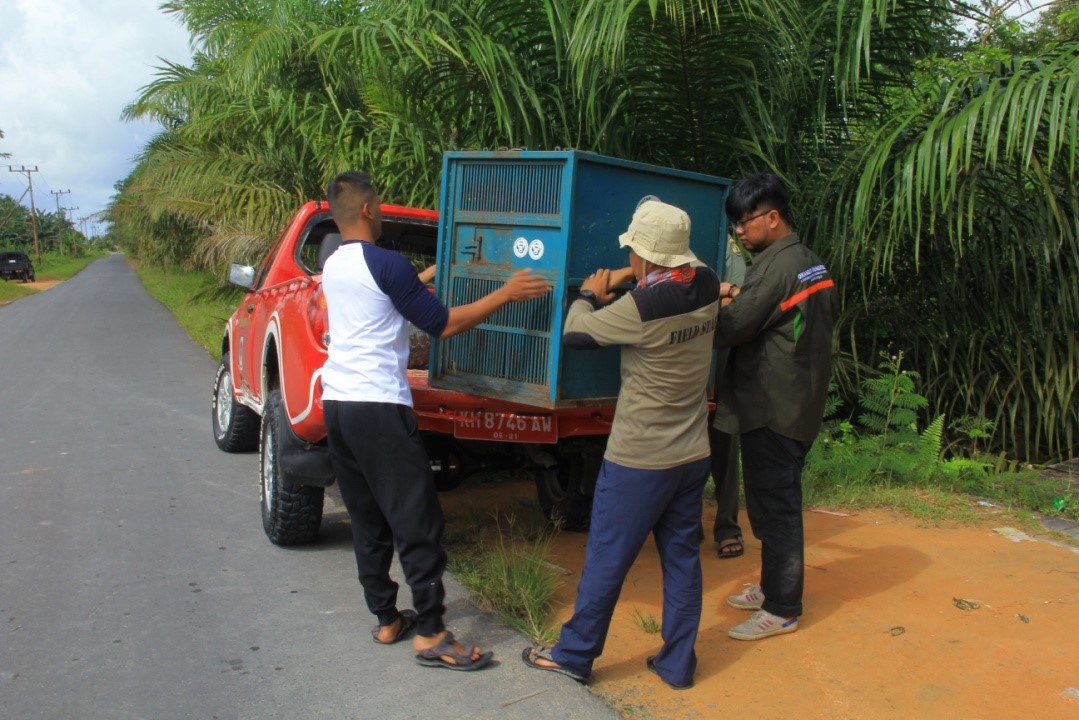
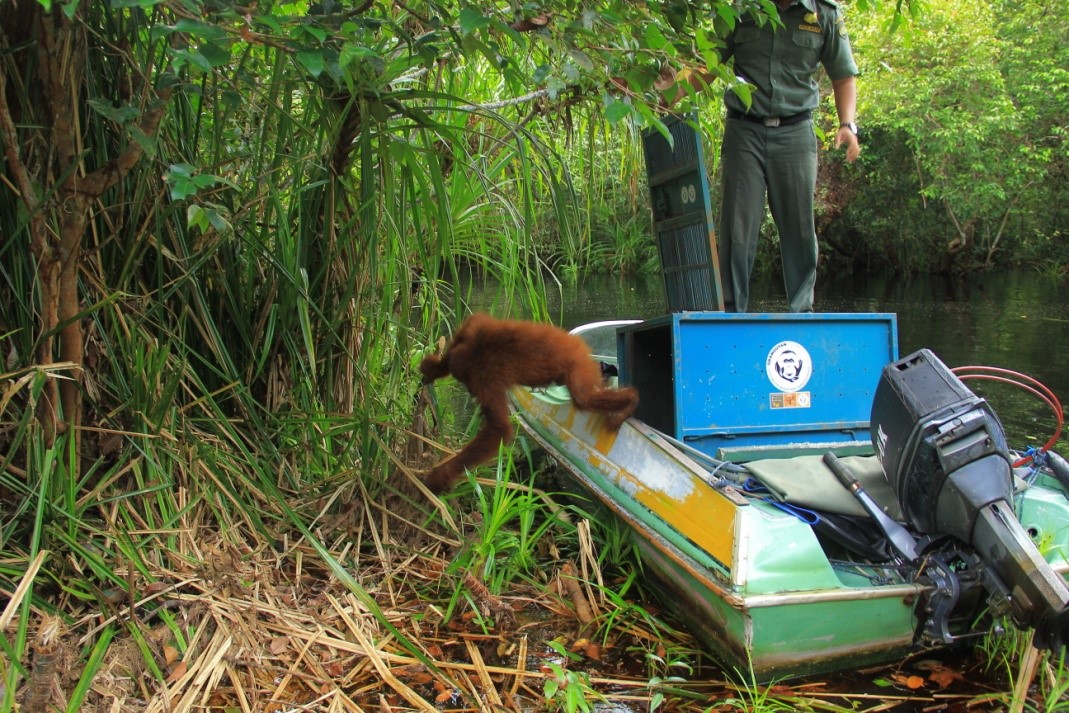
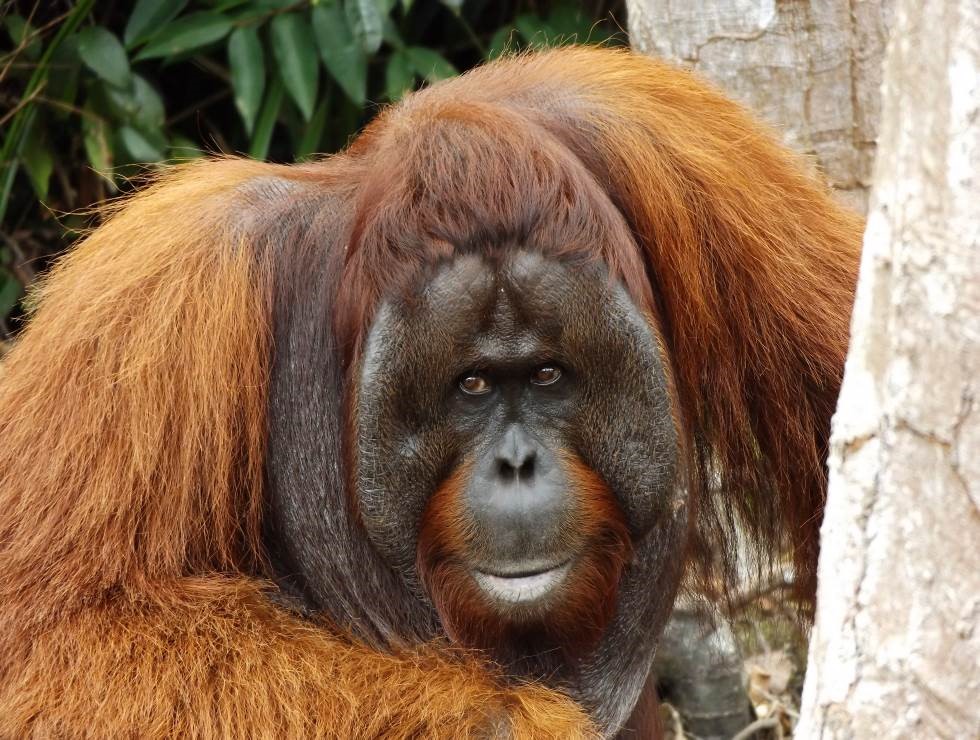
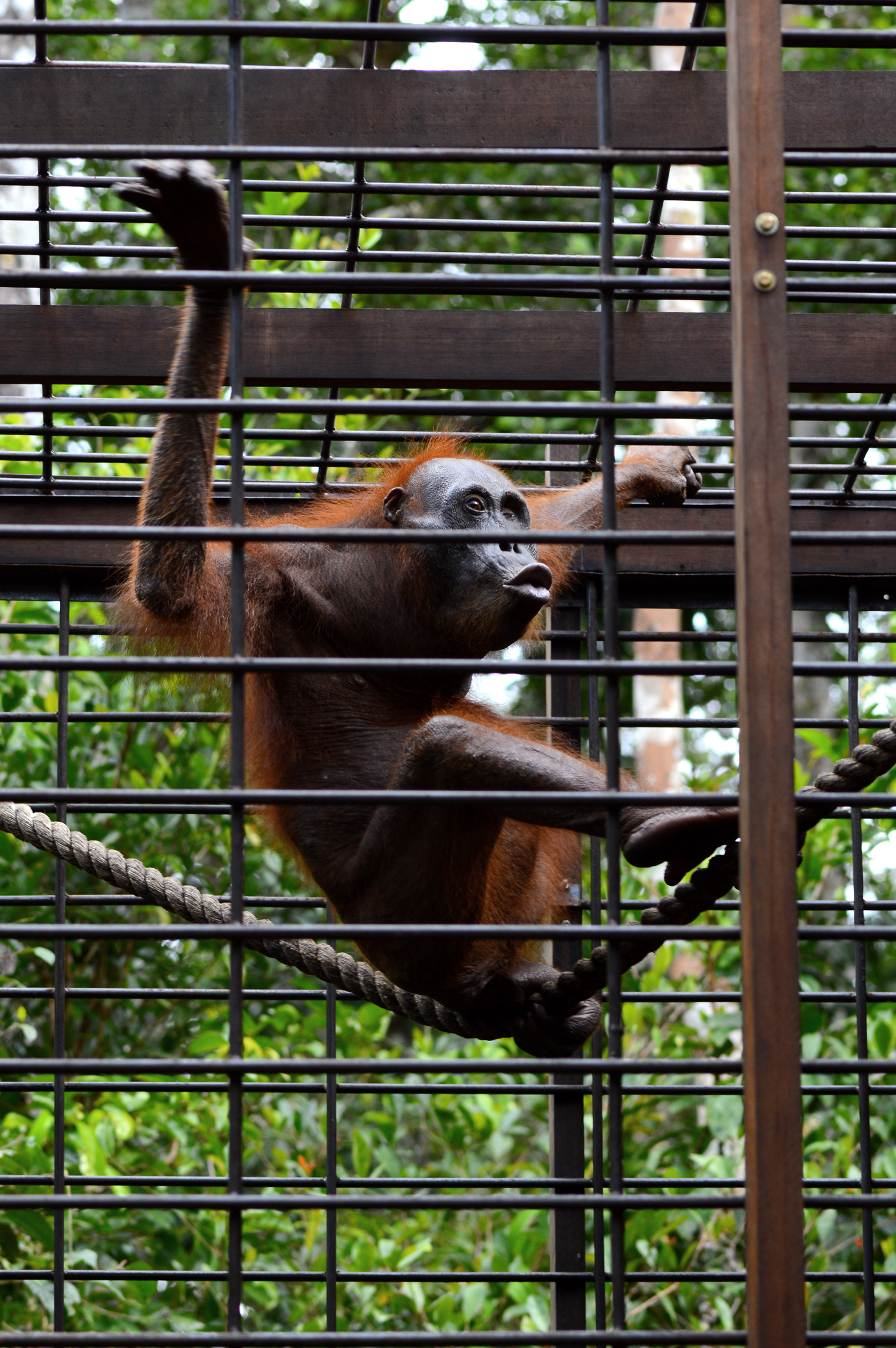
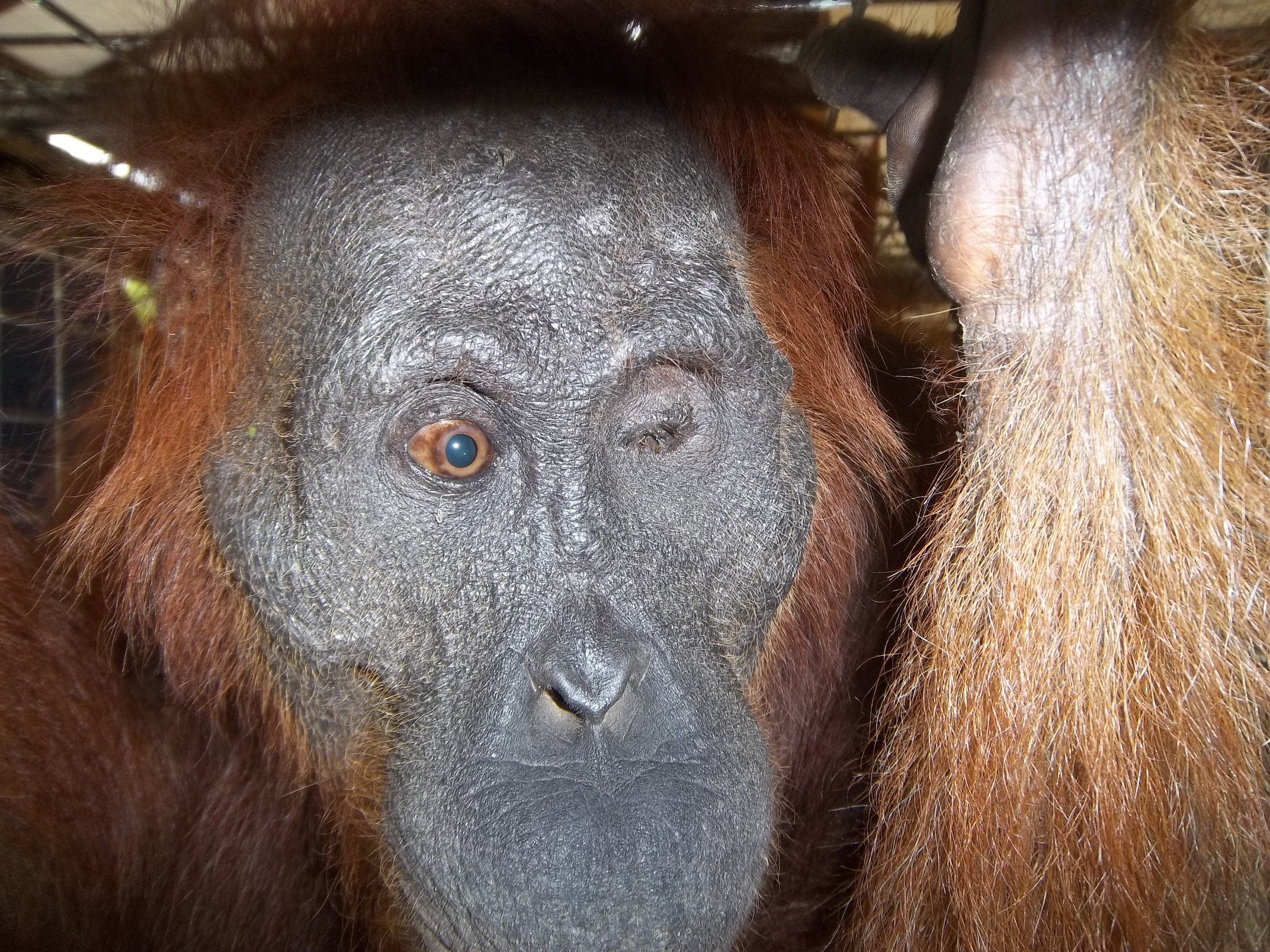
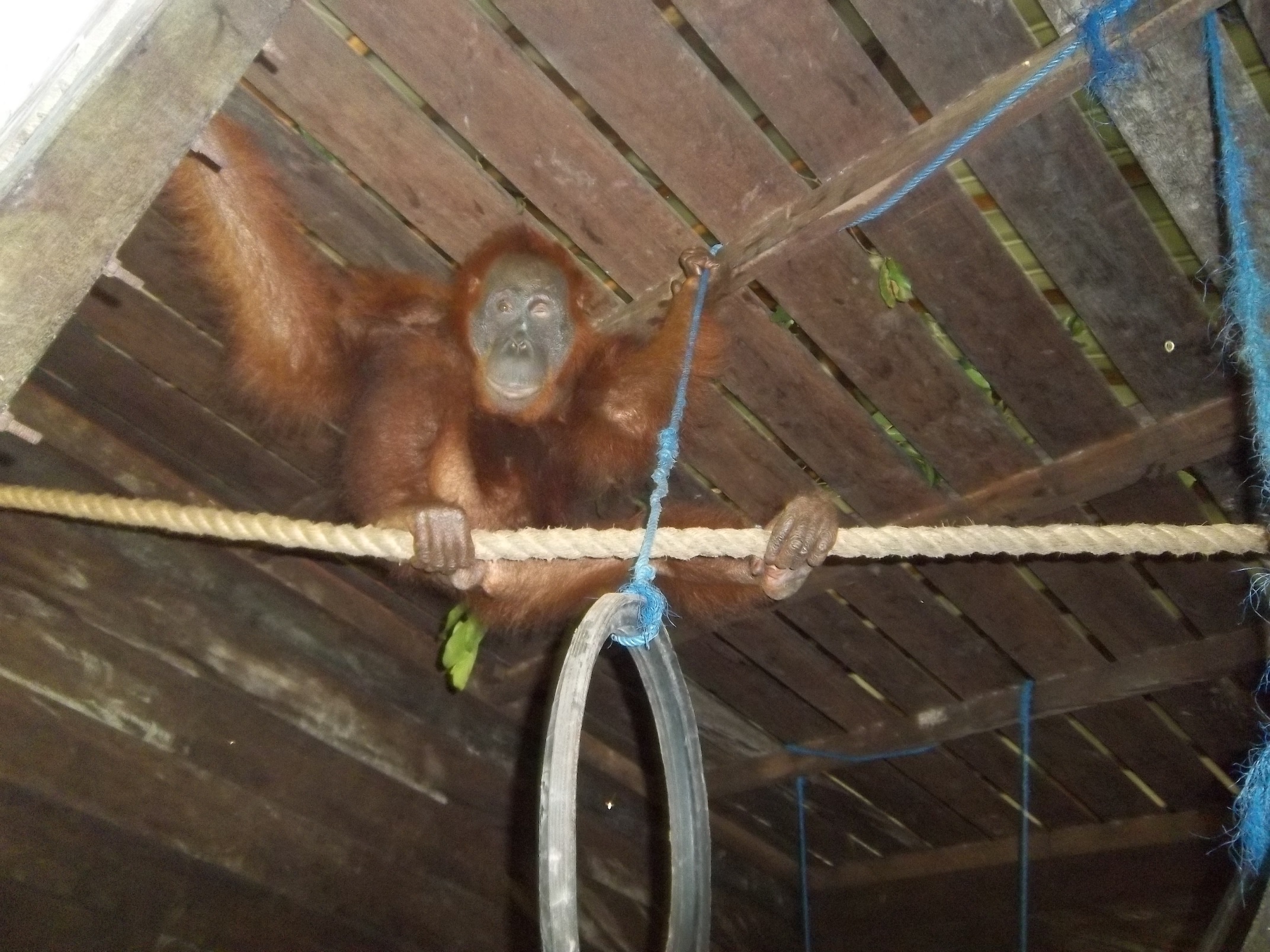
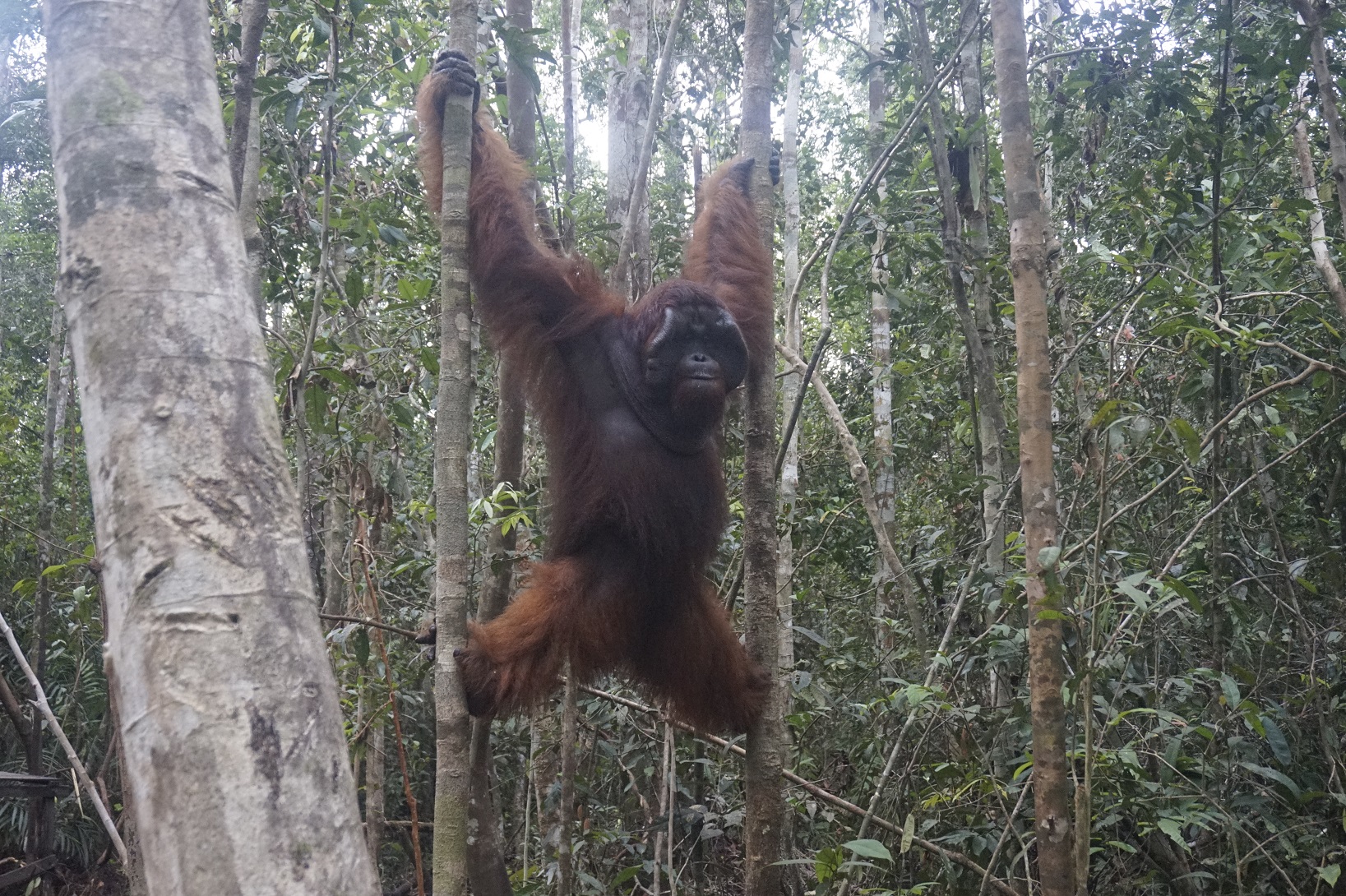
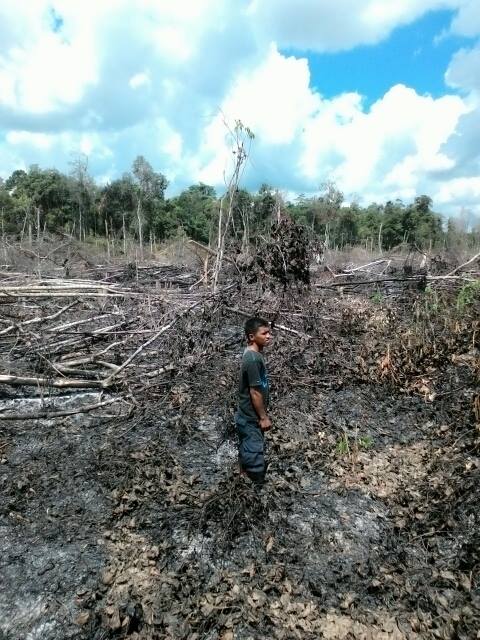
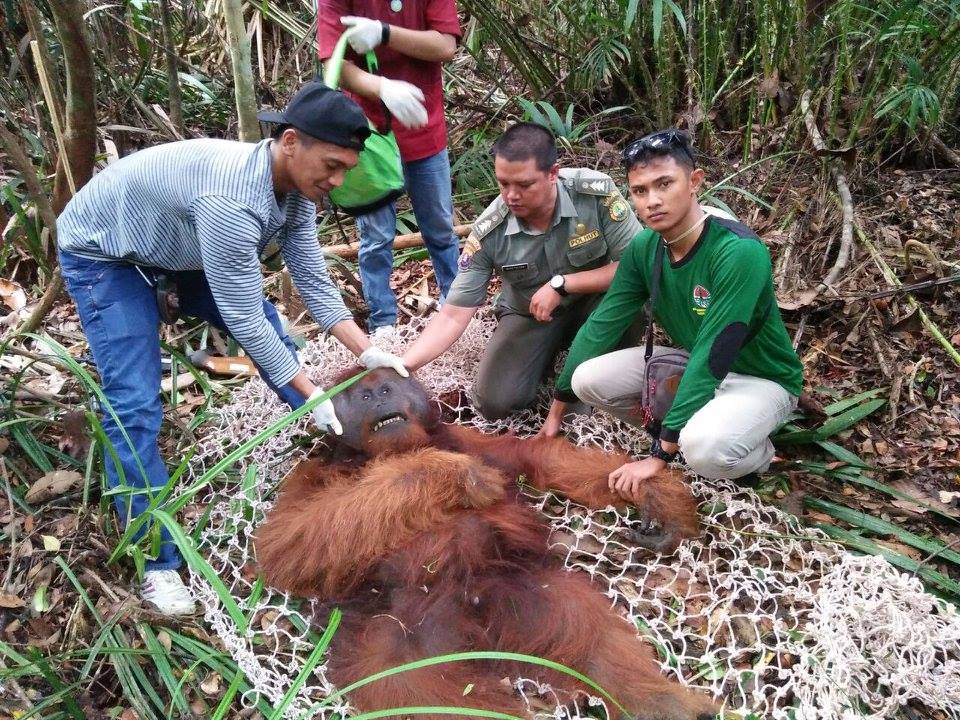






































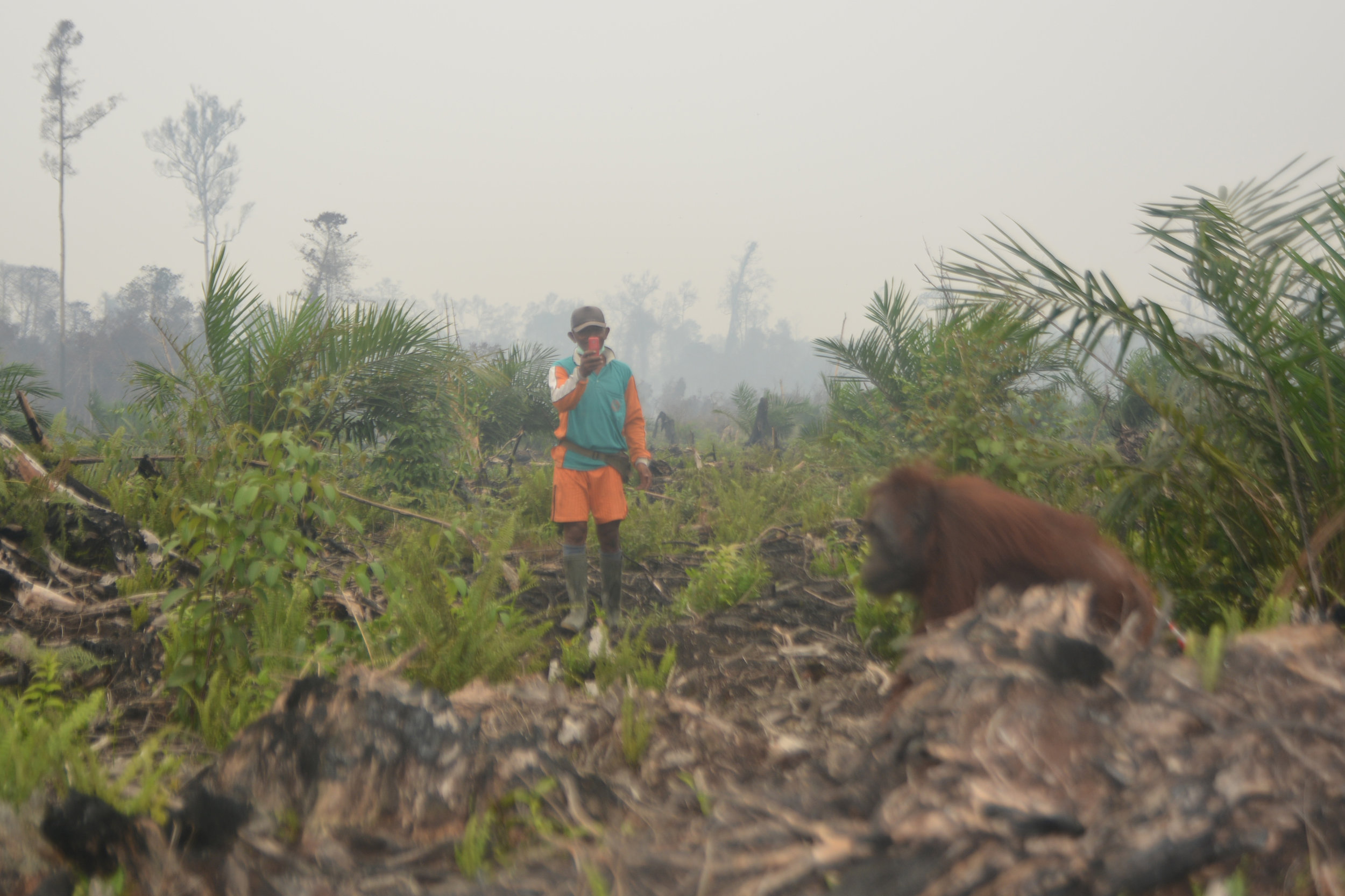
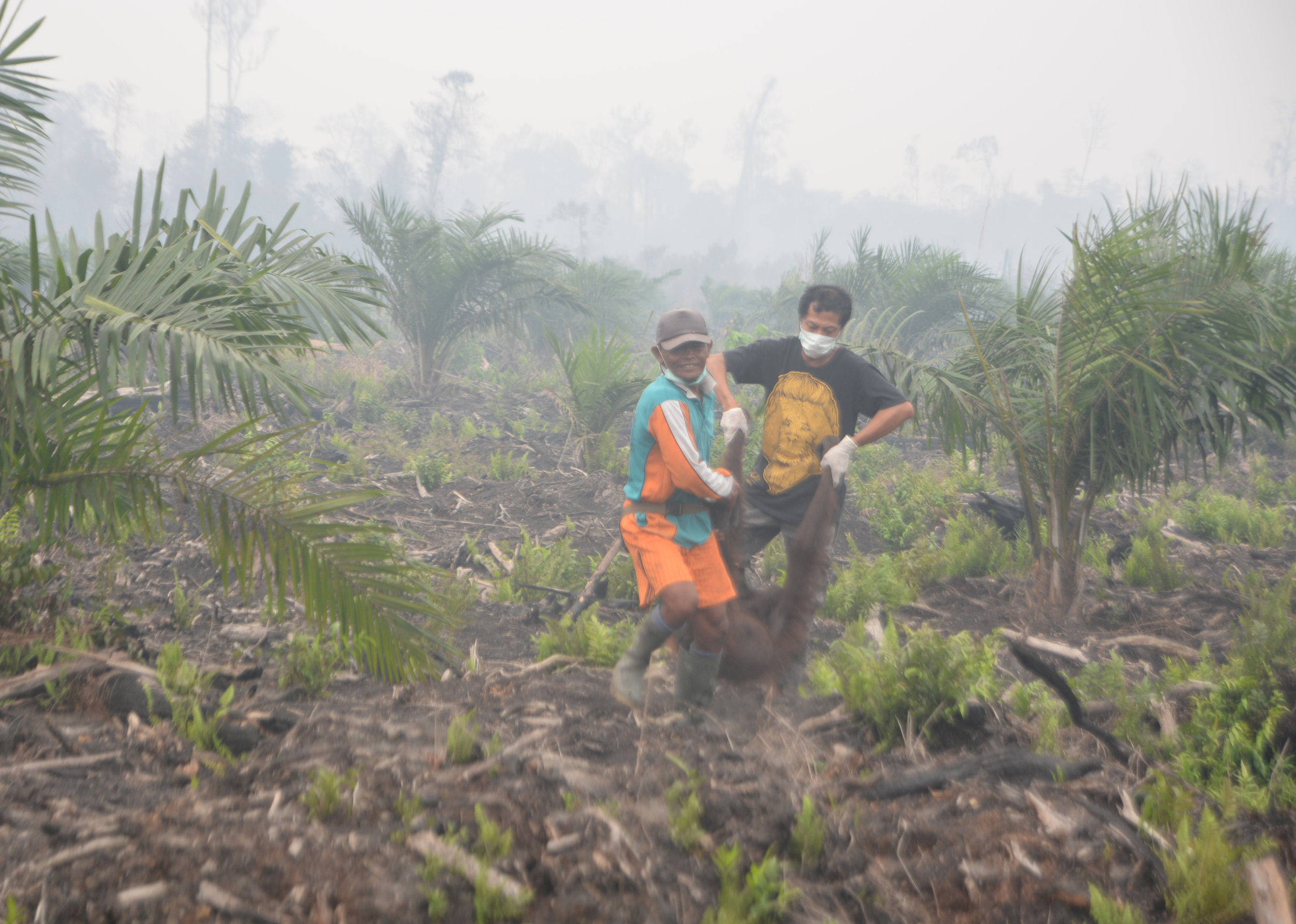
 On Monday, 28th August 2017, Orangutan Foundation together with the local wildlife authority, managed to rescue an orangutan, found stranded in a forested area between a village and an oil-palm plantation in Central Kalimantan. The orangutan, an adult male of around 17 years of age, only weighed 80kg - about two thirds its expected weight..
On Monday, 28th August 2017, Orangutan Foundation together with the local wildlife authority, managed to rescue an orangutan, found stranded in a forested area between a village and an oil-palm plantation in Central Kalimantan. The orangutan, an adult male of around 17 years of age, only weighed 80kg - about two thirds its expected weight..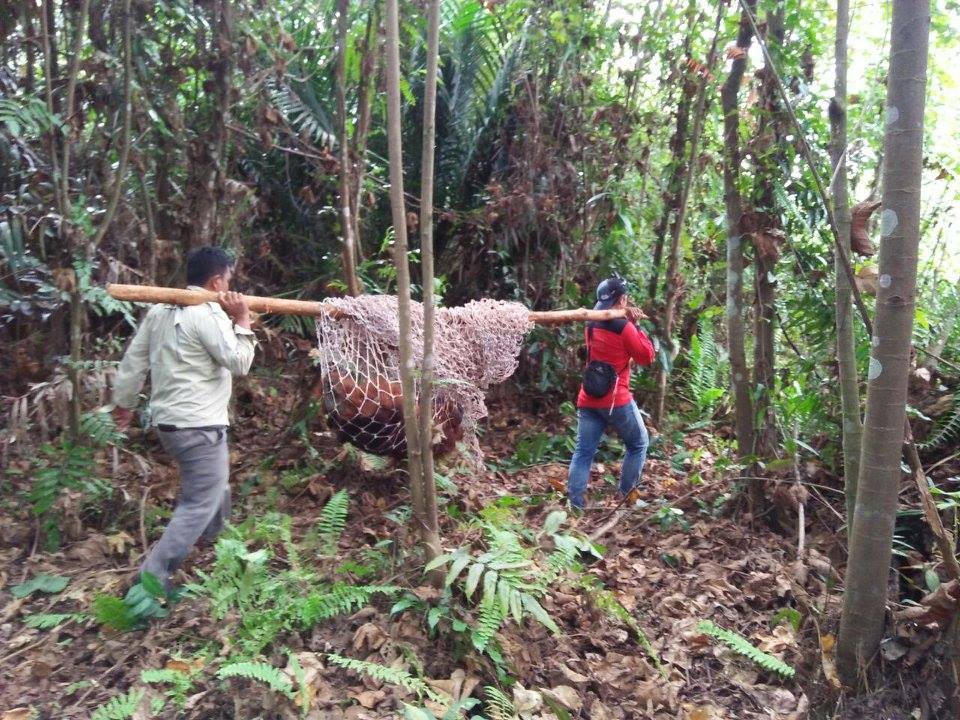






 We have seen two orangutan births in less than two months. Why is this significant and a reason to celebrate? Orangutans are critically endangered, a recent report found that orangutan populations on Borneo have declined by 25% over the last 10 years. A shocking statistic. However, in the
We have seen two orangutan births in less than two months. Why is this significant and a reason to celebrate? Orangutans are critically endangered, a recent report found that orangutan populations on Borneo have declined by 25% over the last 10 years. A shocking statistic. However, in the 




















