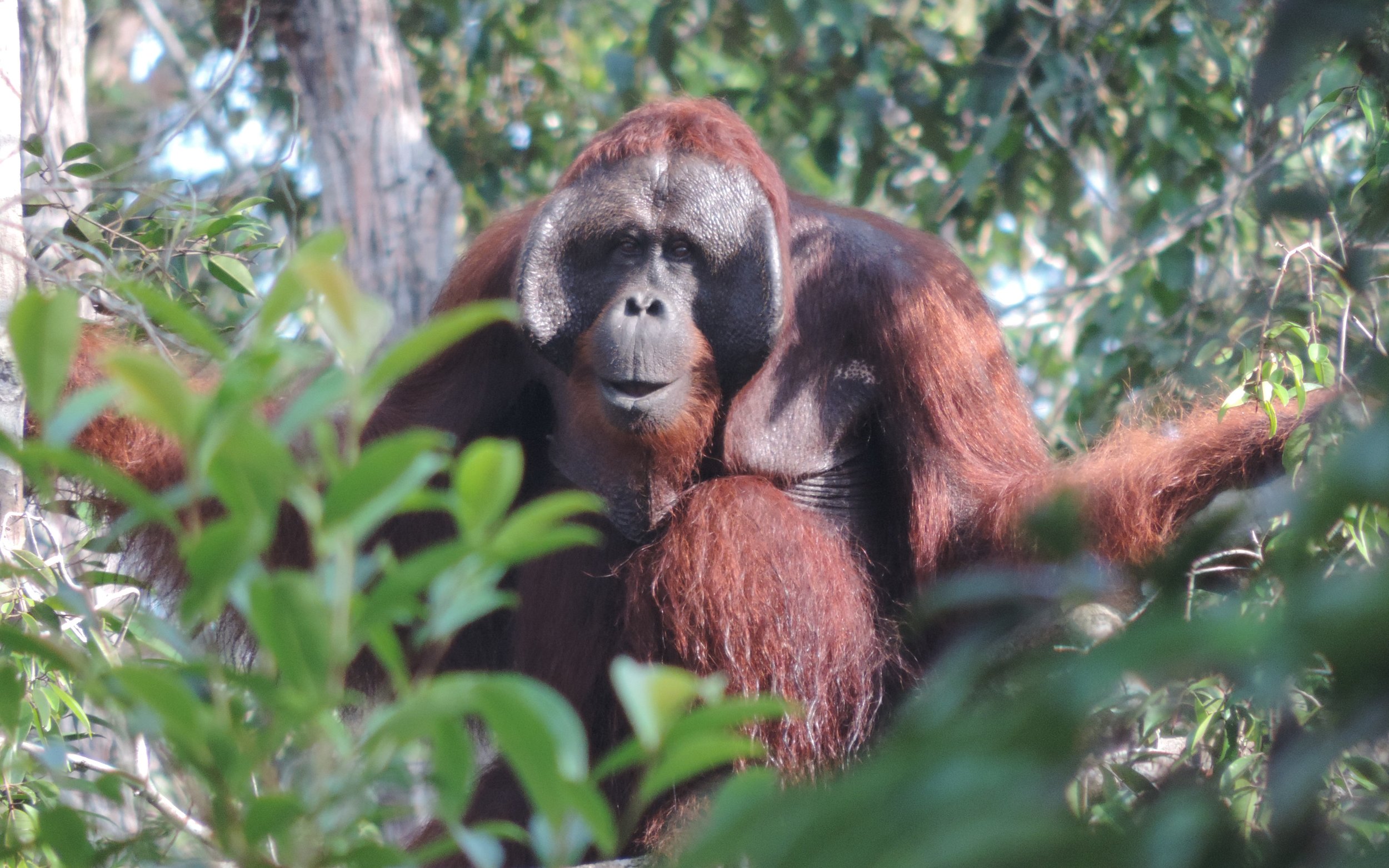
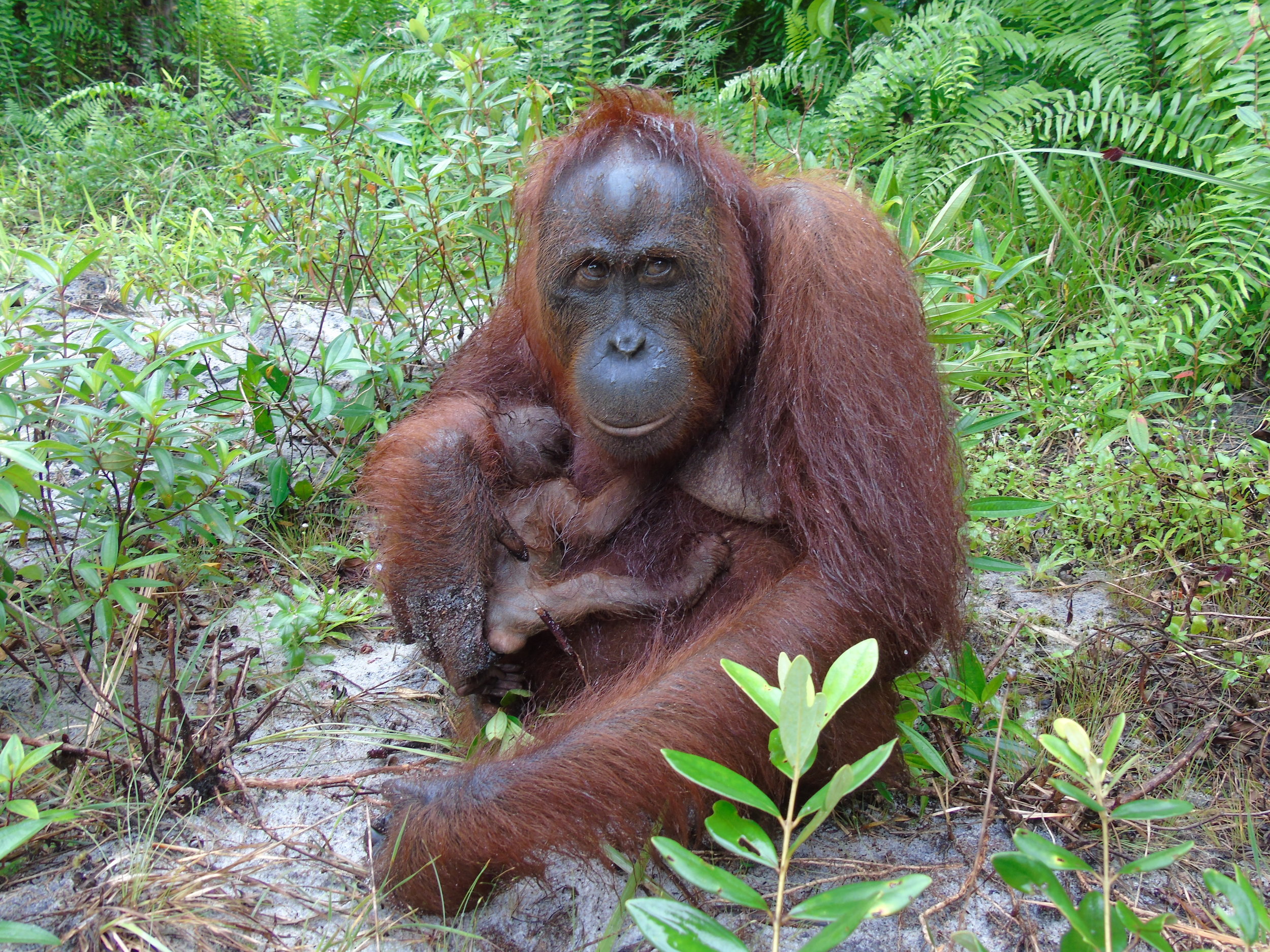
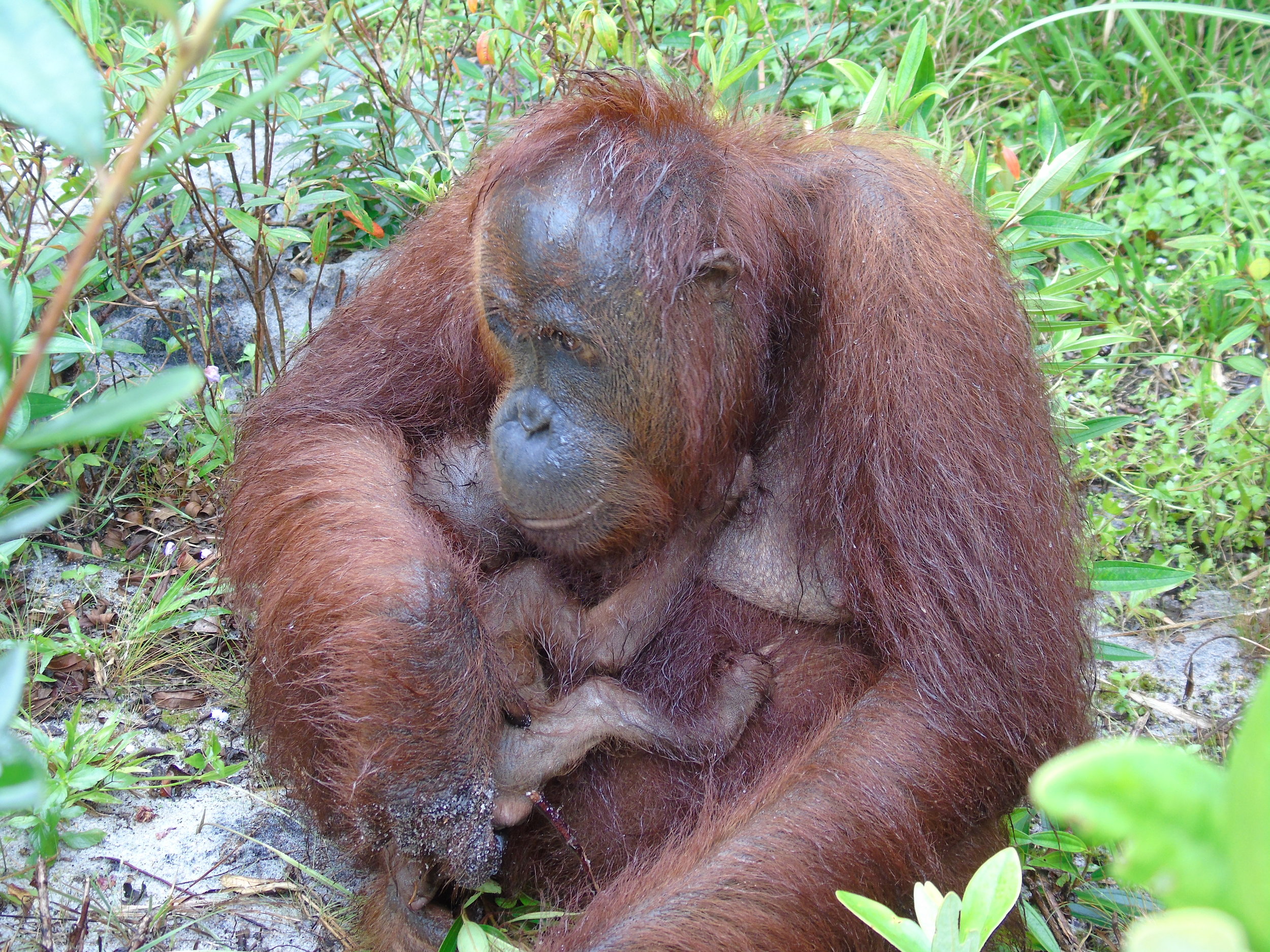
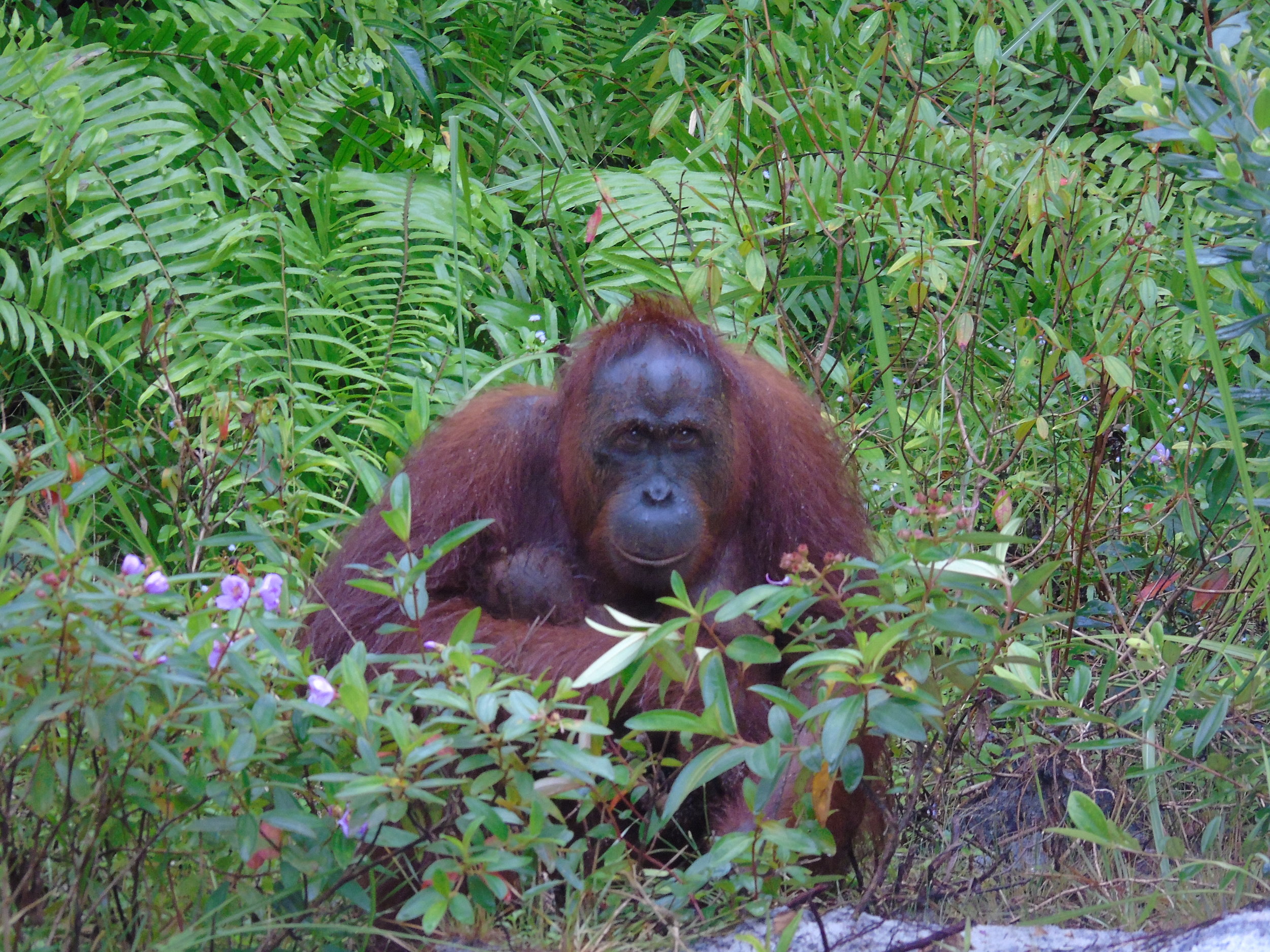
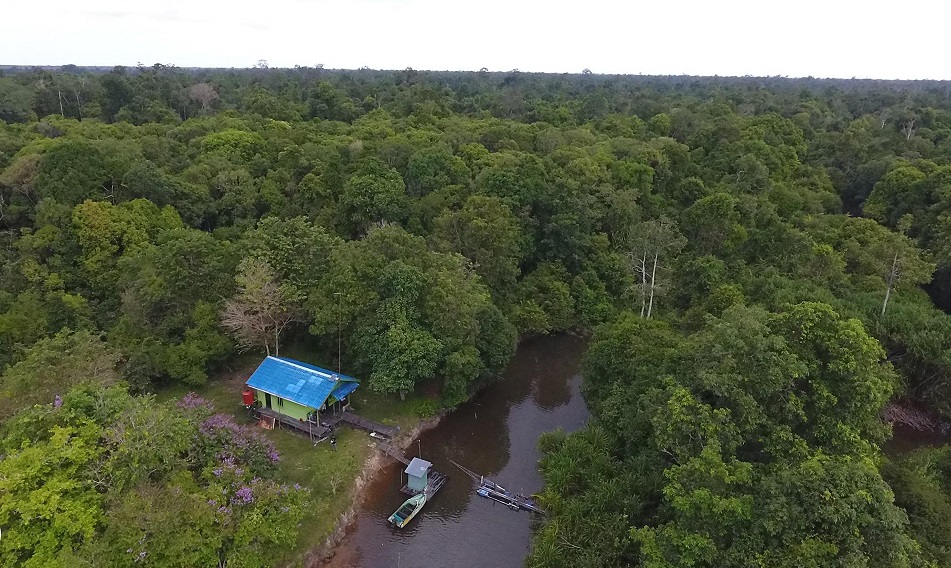
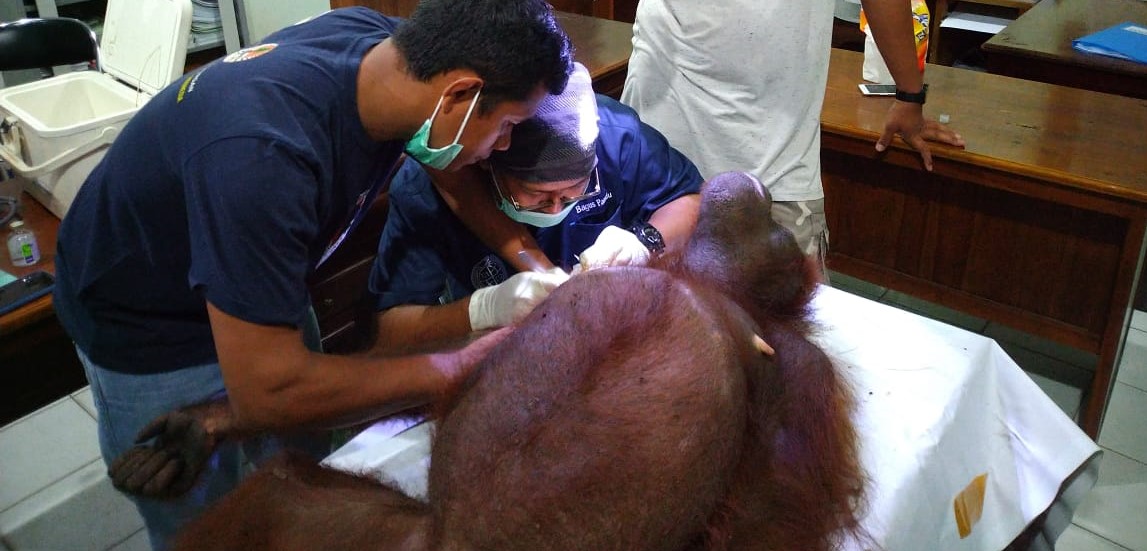
Each month we will be unveiling a story about the orangutans we care for at the Orangutan Foundation, and this month we focus on Pegi. Pegi is an adventurous young orphan who in her short time with us has transformed from a shy and nervous orangutan to one that is confident in the trees. So much so that recently Pegi evaded our team at Camp Buluh for two nights and stayed in the forest on her own for the very first time under the watchful eye of our team.
Pegi before she was rescued as a pet, and after she entered the Foundation’s soft-release programme.
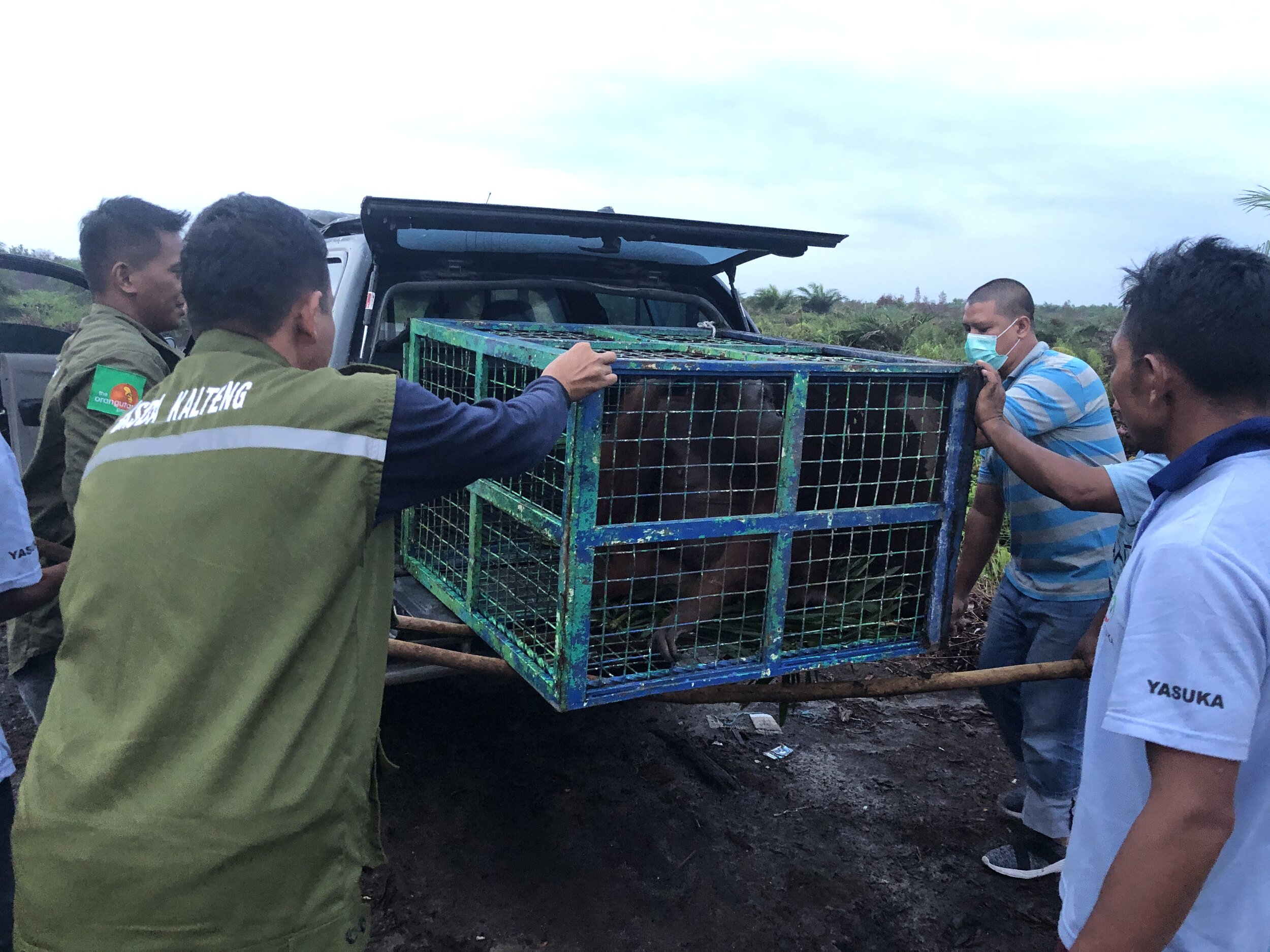
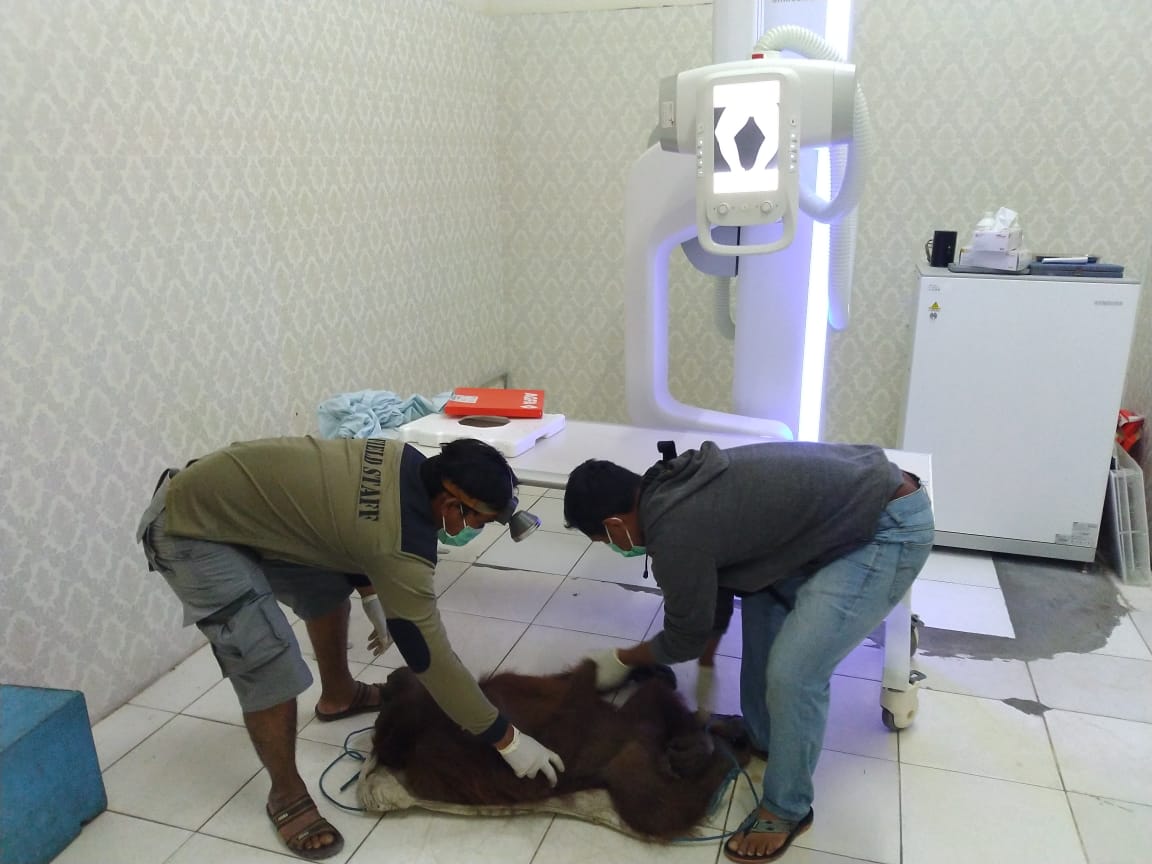
Before entering our orangutan soft release programme within the Lamandau Wildlife Reserve, 8-year-old Pegi was a pet. In August 2019 she was handed over to government officials and Orangutan Foundation staff having spent the previous seven years alone inside a cramped wooden cage, during which time she was never released. She was also fed on a diet consisting of rice, noodles, fruit, and sugary drinks, conditions far from acceptable for a young critically endangered primate.
Spending so many years away from a forest it might be understandable to assume that Pegi would have lost any natural impulses, but as she is proving to our team of orangutan assistants, her wild instincts are very strong and she is quickly understanding and practising the skills necessary for a life in the wild.
When Pegi first arrived at our soft-release site in the forest, she was anxious of the water around camp. Now, one of her favourite things to do is take a gulp of water and spray it into the air!
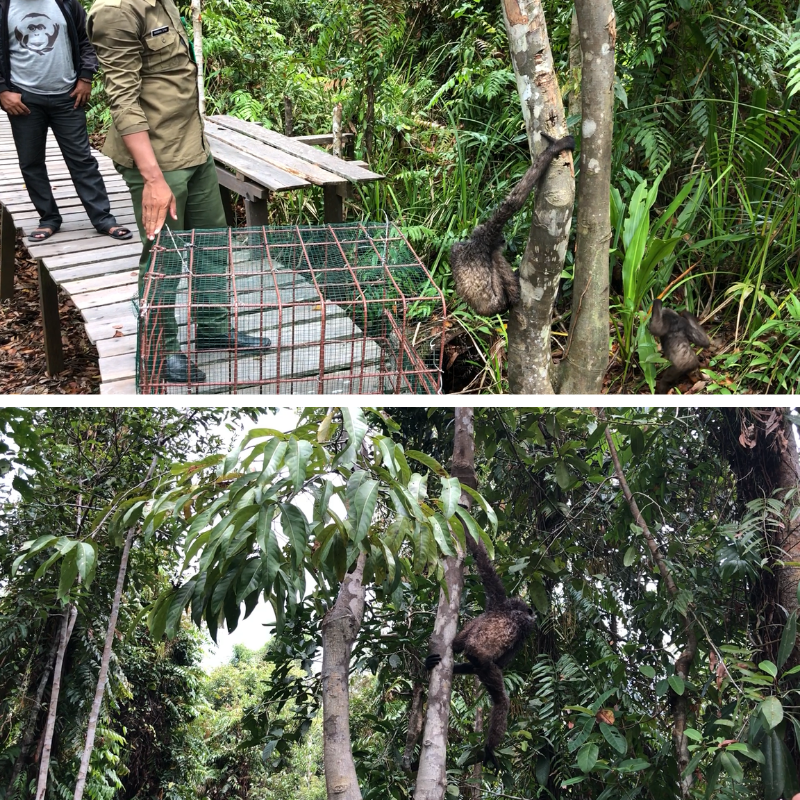
On the morning of the 26th April, Pegi was taken out of her overnight enclosure by our team as usual to allow her to climb in the trees, eat bark, and play in the water. However later that morning Pegi decided to explore a little further than normal and follow a reintroduced female orangutan named Sugih into the forest.
Our team struggled to keep an eye on Pegi as she played high in the canopy, but in the afternoon she did something to surprise everyone, she began making her own nest. This is something that Pegi has never been observed doing before at camp, and sheltering from the rains that had swept over the forest, our team where amazed to see Pegi stay in her nest and sleep in the trees alone for the first time overnight.
With Orangutan Foundation staff keeping watch from below, Pegi continued her adventure through the forest the following day. Playing in Sugih’s nest and climbing from tree to tree, Pegi was observed eating young leaves, flowers, and fruits before adding more branches to her previous nest and settling down for another night in the forest.
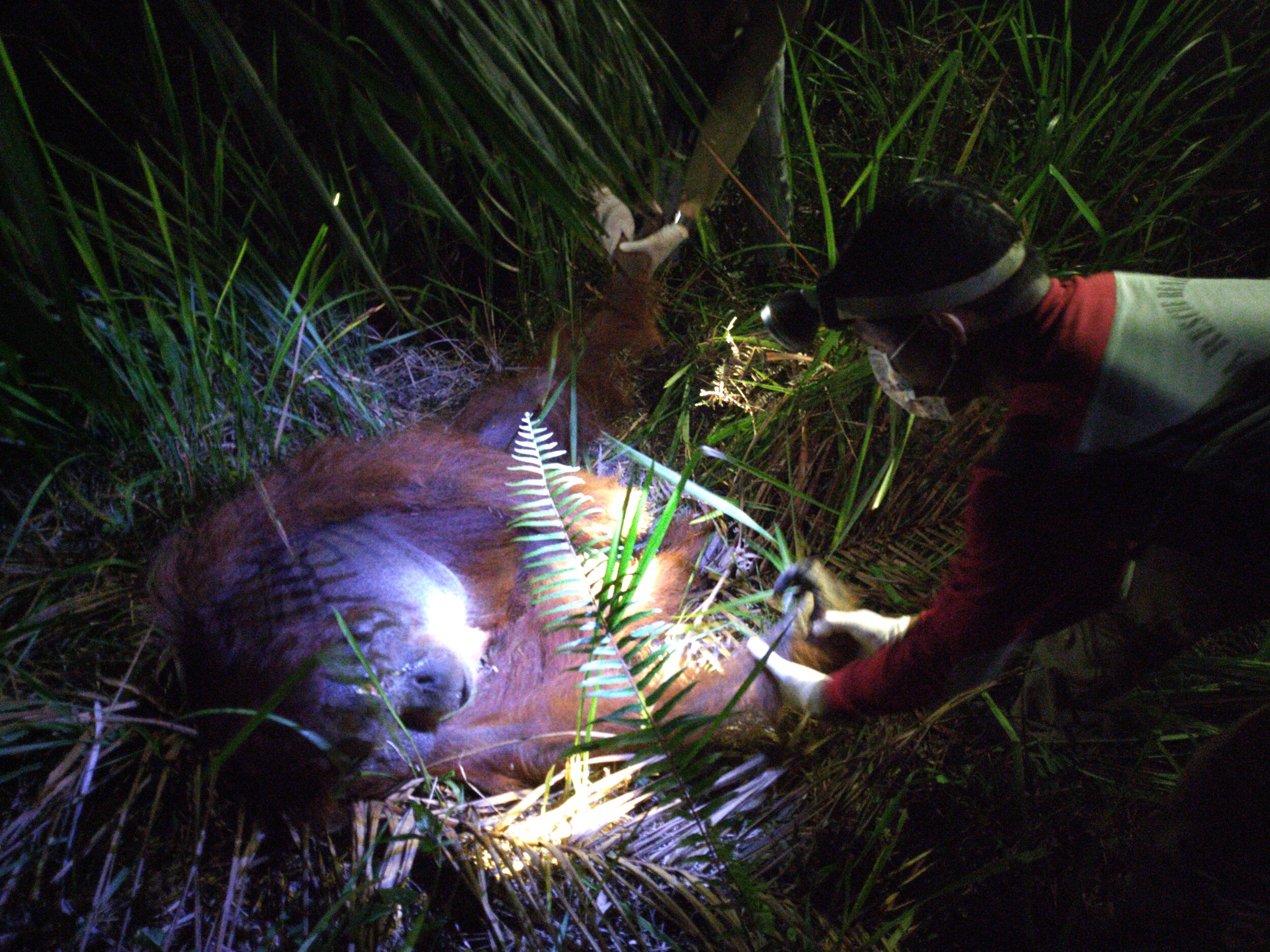
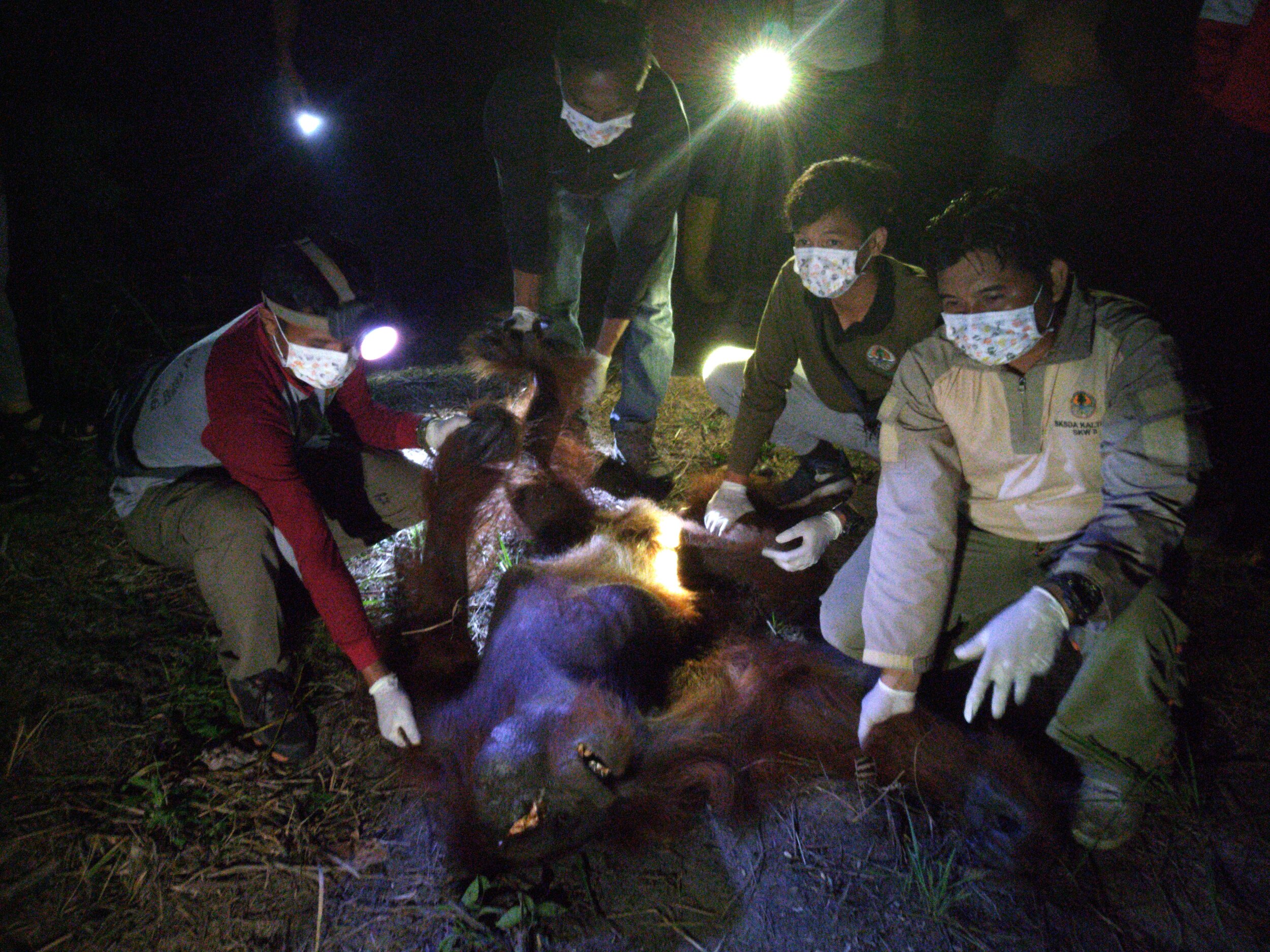
This independent experience for Pegi shows how much she has progressed since her arrival last summer, however there are still abilities that need to be mastered before she is fully prepared for a life in the wild. With this in mind, our team were able to climb up Pegi’s tree on the afternoon of the 28th April and transport her back to camp where she can complete her education.
Pegi certainly appears to have the instincts for a future in the forest, and we hope that by refining her skills with fellow orphaned orangutan Okto, the pair will soon be able to be released from Camp Buluh together into the protected Lamandau Wildlife Reserve.